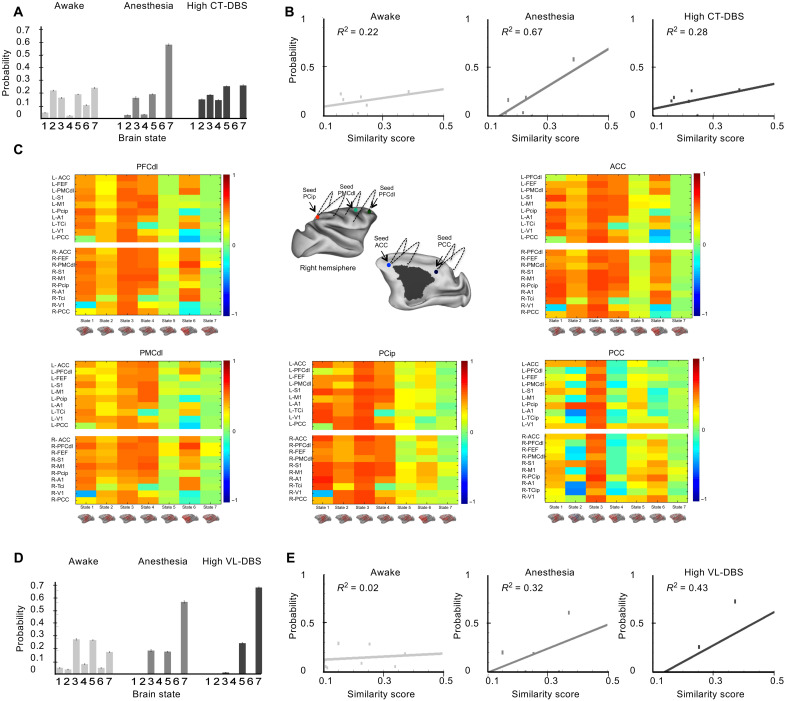
Fig. 5. Central thalamic stimulation restores dynamic connectivity in anesthetized macaques.
Effects of high CT-DBS (A to C) or high VL-DBS (D and E) on dynamic connectivity of the cortex. Unsupervised clustering of the covariance FC matrix revealed seven brain states, which are sorted according to their similarity to the structural connectivity matrix. (A) Probability distributions of brain states for the awake state, anesthesia, anesthesia + high CT-DBS clustering. Each bar represents the within-condition probability of occurrence of a state. (B) Probability of occurrence of each brain state as a function of the similarity between FC and structural connectivity for the awake state, anesthesia, and anesthesia + high CT-DBS. (C) Changes of FC across the seven brain states between the GNW and its remaining areas such as PFCdl, PMCdl, Pcip, ACC, and PCC. On the x axis, brain states 1 to 7. On the y axis, studied ROIs of the macaque GNW [ACC, PFCpol (polar prefrontal cortex), FEF, PMCdl, S1, M1, Pcip, A1, TCi, V1, and PCC of the left (L) and right (R) hemisphere] connected to the seed. (D) Probability distributions of brain states for the awake state, anesthesia, anesthesia + high VL-DBS. Each bar represents the within-condition probability of occurrence of a state. (E) Probability of occurrence of each brain state as a function of the similarity between FC and structural connectivity for the awake state, anesthesia, and anesthesia + high VL-DBS. Primary somatosensory cortex (S1); primary motor cortex (M1); primary auditory cortex (A1); inferior temporal (TCi); visual area 1 (V1).