Figure 3.
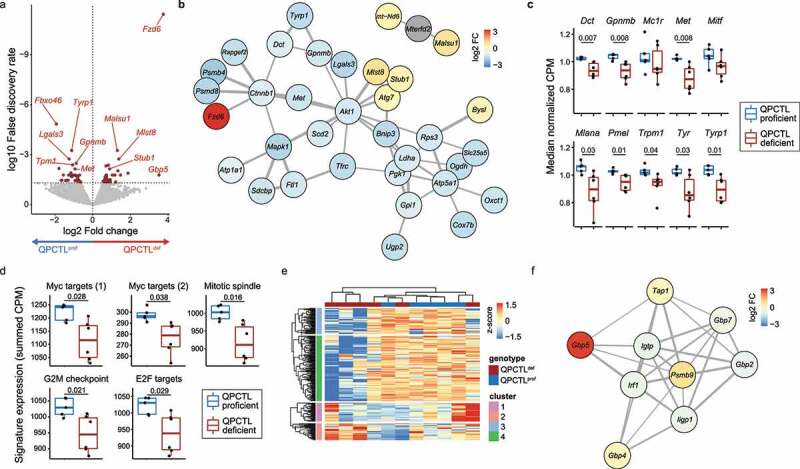
QPCTL deficiency results in suppression of melanogenesis and cell metabolism. mRNA sequencing was performed on sorted CD45-negative cells from QPCTL-proficient (n = 5) and QPCTL-deficient (n = 6) B16F10 TMEs. Tumors were harvested at day 14 post inoculation. (a) Differential gene expression analysis comparing CD45-negative cells obtained from QPCTL deficient versus QPCTL-proficient TMEs. Genes with a false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 are indicated in red. Selected genes are indicated in the plot. (b) network analysis (StringDB) performed on all significantly (FDR < 0.05) differentially expressed genes. Genes with a medium interaction strength (> 0.4) are included. Line thickness indicates interaction strength. Nodes are colored based on log2 fold differences obtained in a. (c) Transcript abundance of selected genes in the melanogenesis pathway. Boxplots indicate group median and 25th /75th percentiles, whiskers indicate the interquartile range multiplied by 1.5, dots signify individual samples. (d) Signature expression of cell cycle-associated hallmark signatures from MSigDB, calculated as the summed CPM of all genes within each signature. Boxplots indicate group median and 25th /75th percentiles, whiskers indicate the interquartile range multiplied by 1.5, dots signify individual samples. (e) Hierarchical clustering of the 1,000 most differentially expressed genes across all samples, depicted as a row-normalized heatmap. (f) Network analysis (StringDB) performed on genes from cluster 2 (e). Genes with a medium interaction strength (> 0.4) are included. Line thickness indicates interaction strength. Nodes are colored based on log2 fold differences obtained in panel a. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test (c, d). Significant P values (< 0.05) are indicated in the plots. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. CPM, counts per million; MSigDB, Molecular Signatures Database.
