Figure 8.
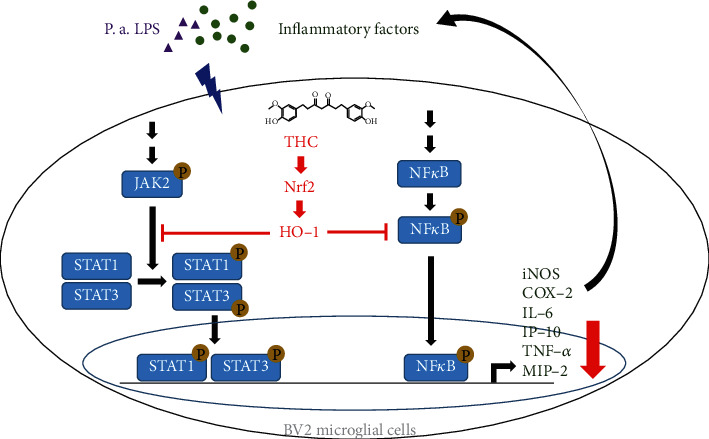
Conclusion of this study. THC blocks P. a. LPS–induced oxidative responses by increasing Nrf2-HO-1 expression which attenuates the iNOS, COX-2, and p-NFκB expression. THC also inhibits the level of P. a. LPS–prompted JAK-STAT signaling and the inflammatory mediators IL-6, TNF-α, MIP-2, and IP-10 productions. Collectively, THC is a potent anti-inflammatory agent in brain encephalitis.
