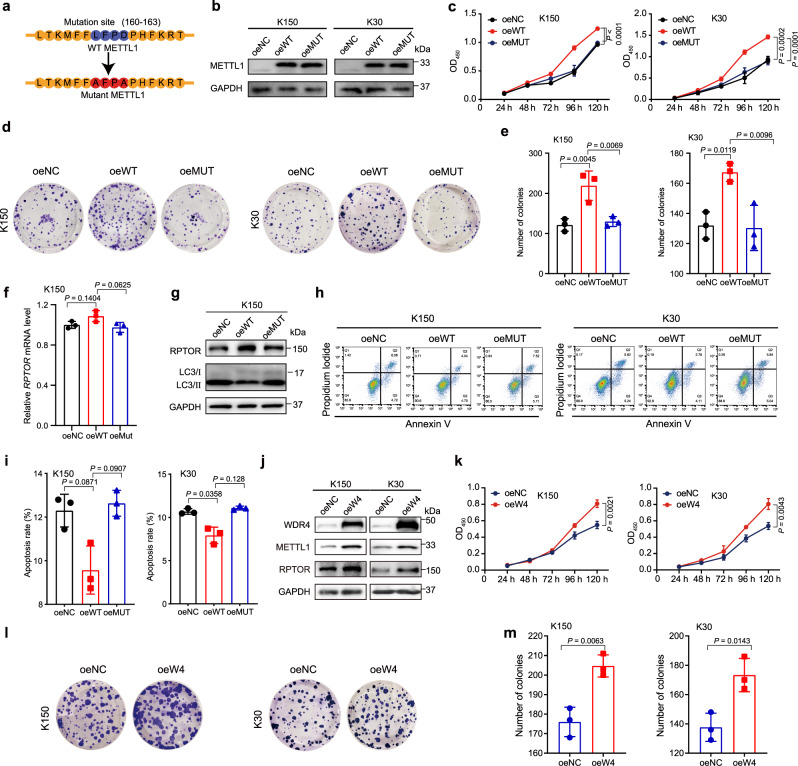
Fig. 6. Overexpression of METTL1 or WDR4 promotes ESCC progression.
a The catalytic mutation site of METTL1. b Western blot confirmed the overexpression of wild-type METTL1 (oeWT) and catalytic inactive METTL1 (oeMUT) compared with the negative control (oeNC) in ESCC cells. c CCK8 assay of growth of oeNC, oeWT, and oeMUT ESCC cells. d, e Colony-formation assay (d) and the quantification analysis (e) of oeNC, oeWT, and oeMUT ESCC cells. f qRT-PCR assay of RPTOR mRNA level. g Western blot assay showed the indicated protein levels. h, i Apoptosis assay (h) and the quantitative analysis (i) of METTL1 overexpression and control cells. j Western blot assay showed the indicated protein levels. k CCK8 assay of growth of oeNC and oeWDR4 ESCC cells. l, m Colony-formation assay (l) and the quantification analysis (m) of oeNC and oeWDR4 ESCC cells. Data represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. P values are presented by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for (c, e, f, and i), and two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test for (k and m).