Figure 7. Brain mediators of the relation between pain catastrophizing and threat-safety discrimination.
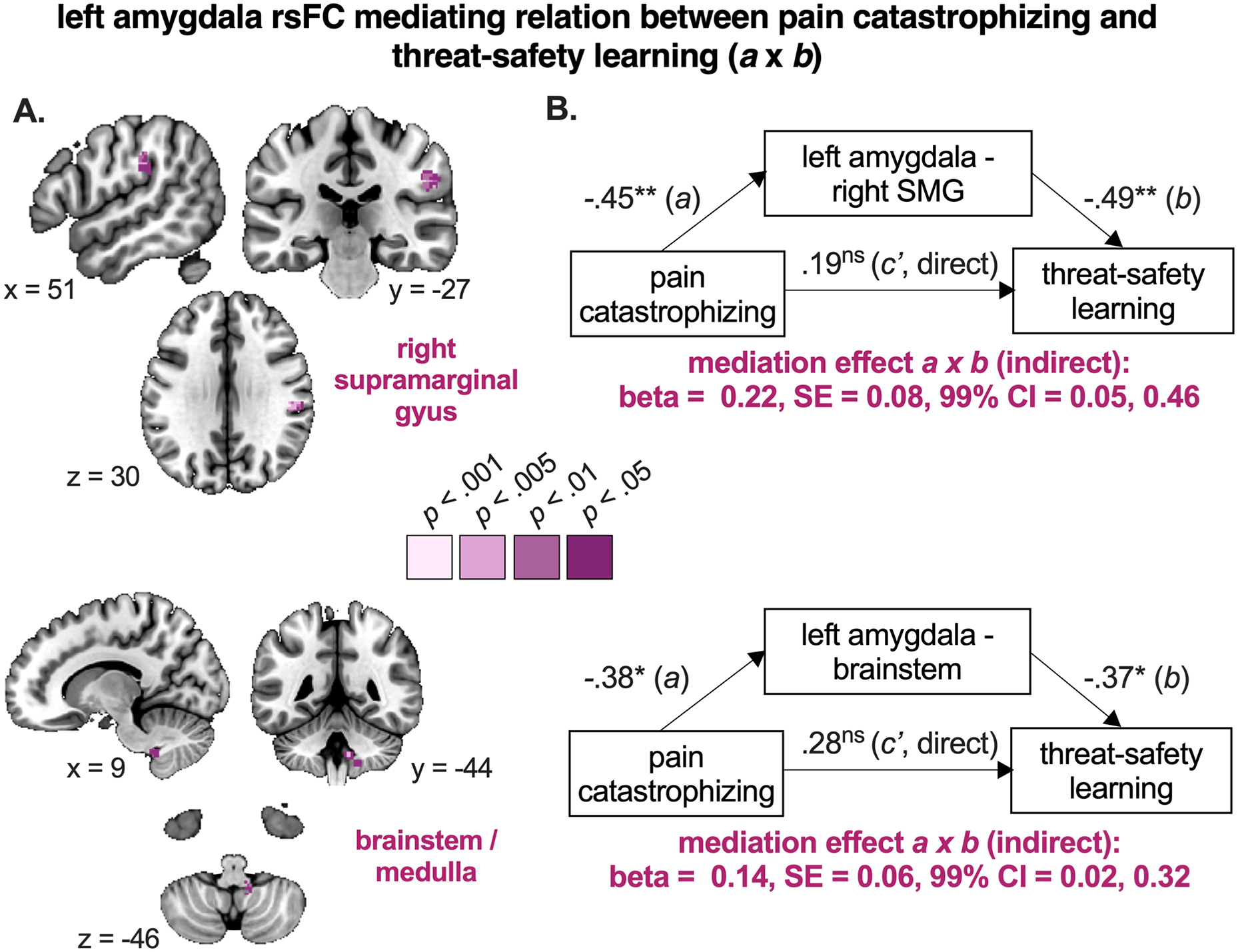
A. Brain regions in purple are significant mediators of the relationship between pain catastrophizing and threat-safety learning, meaning that stronger associations between pain catastrophizing and threat-safety discrimination learning are mediated by reduced left amygdala coupling with right supramarginal gyrus and brainstem. Note that only clusters surviving p < .001 are presented, along with their surrounding subthreshold data. B. The path diagrams and standardized coefficients are presented for descriptive purposes, as calculated offline (post-hoc). See Table S9 for more details. SE = standard error, CI = confidence interval. * p < .01, ** p < .005, *** p < .001, ns p > .05 (not significant)
