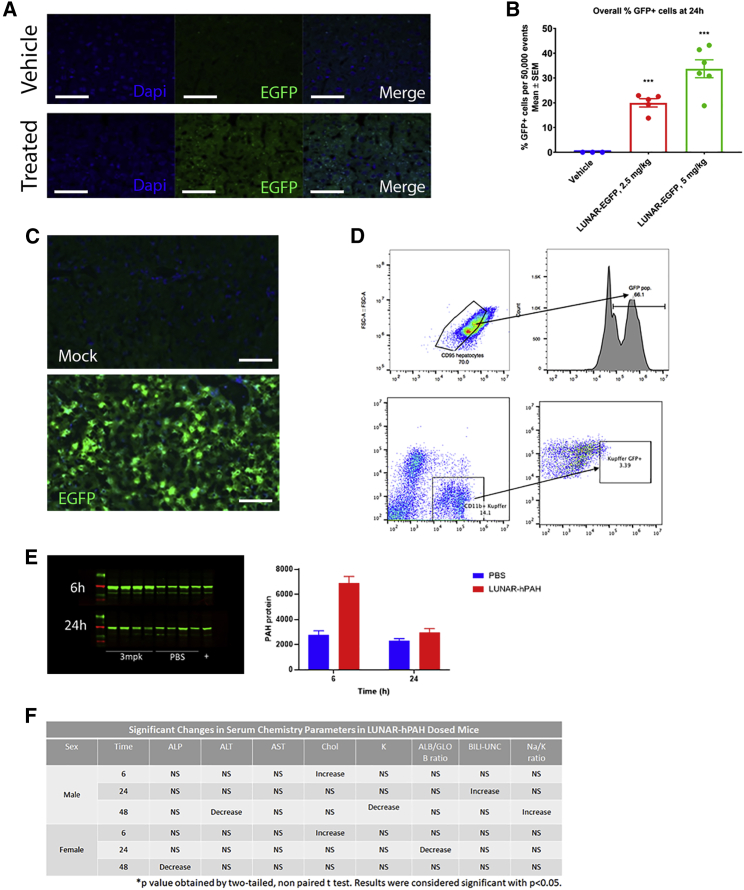
Figure 3.
Delivery of LUNAR-mRNA (LUNAR1) carrying codon-optimized hPAH or EGFP mRNAs to hepatocytes in WT mice
(A) PAH protein detection by immunofluorescence (green) in vehicle or LUNAR-EGFP-treated mice.
(B) Images were quantified (n = 3–6, ∗∗∗p = 0.0001) and normalized by the number of nuclei (DAPI, blue stain on B). (C) Hepatocyte cells isolated from untreated and LUNAR-EGFP-treated mouse livers by cell sorting were imaged to detect EGFP fluorescence. (D) FACS analysis of mouse livers to identify the percentage of hepatocytes (top, CD95/EGFP) or non-hepatocytes (bottom, CD11b/EGFP) that have been targeted by LUNAR-EGFP (n = 5 mice per group in D and E). (E) Protein expression analysis by western blot (left) and quantification (right graph) of PAH levels in the liver of WT mice after 6 and 24 h post-dose with either PBS or 3 mg/kg of LUNAR (n = 4 mice per group). (F) Clinical chemistry to evaluate effect of LUNAR-hPAH mRNA (LUNAR1) delivery in liver and kidney markers: ALT, ALP, potassium, albumin, globulin, cholesterol, bilirubin, sodium (n = 15 mice per group). Scale bars, (A) 50 μm, (C) 30 μm.