Figure 4.
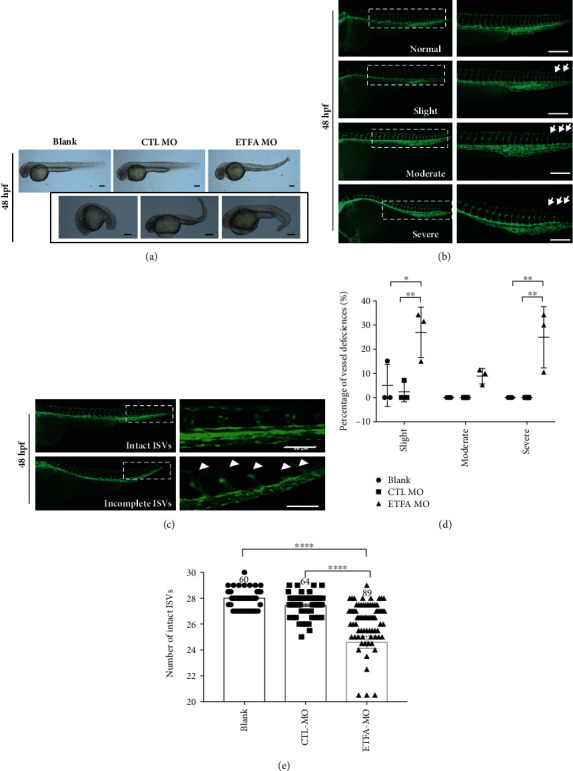
ETFα knockdown induced deformities at 48 hpf. (a) Representative bright field images showing different types of deformities in ETFA-MO-injected Tg Flk1: EGFP embryos at 48 hpf. The photographs in the black box exhibit different deformities of ETFA MO-treated larvae; scale bar = 200 μm; (b) representative fluorescent images showing different types of vascular defects in ETFA-MO-injected Tg Flk1: EGFP embryos at 32 hpf. These defects were classified as slight (intact ISVs less than 27 but more than 25), moderate (intact ISVs less than 25 but more than 20), and severe defect (intact ISVs less than 20). The white arrows indicate where the vessel is defective. DLAV: dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel; ISVs: intersegmental vessels; DA: dorsal aorta, scale bar = 100 μm; (c) ETFα inhibition impaired segmental vessel sprouting and their fusion with DLAV in Tg Flk1: EGFP zebrafish larvae at 48 hpf. Data presented here were representative fluorescent images of vascular sprouting defects of segmental vessels; (d) quantitative data of the different vascular defects at 48 hpf (one-way ANNOVA, n = 3); (e) quantitative data of intact ISVs in zebrafish larvae at 48 hpf (one-way ANNOVA, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.00001, n = 60).
