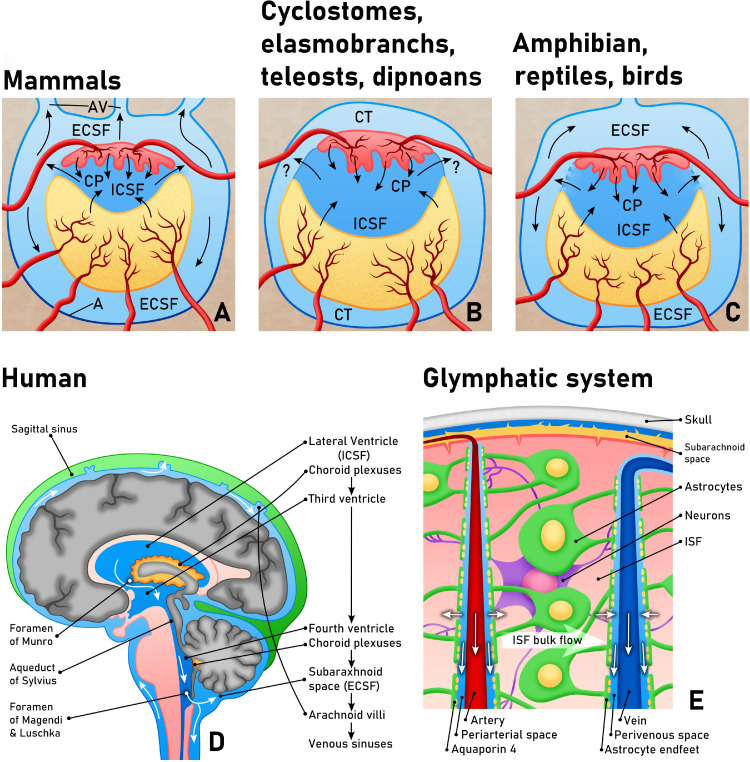
Figure 1.
Evolutionary relationships of CSF and the glymphatic system. A. In mammals, the internal CSF (ICSF) is secreted by the choroid plexus (CP) and is continuous with the external CSF (ECSF) or subarachnoid space via the foramina of the fourth ventricle. B. In cyclostomes, elasmobranchs, teleosts and dipnoans, the ICSF is not in communication with an ECSF compartment but may be able to pass into the pericerebral connective tissue (CT). C. In amphibians, reptiles and birds, there is an absence of a metapore or foramen, however, ICSF is thought to pass through a permeable membrane to reach the ECSF compartment. Note that absorption through arachnoid villi (AV) only occurs in certain mammalian species, as shown in A. Modified from.64 D. CSF circulation in humans, and a closer image of the glymphatic system (E) showing the flow of fluid within the interstitial compartment from periarterial to perivenous spaces in the brain. Astrocytic endfeet make up a significant part of the blood brain barrier and aquaporin-4 has been shown to regulate extracellular fluid volume.