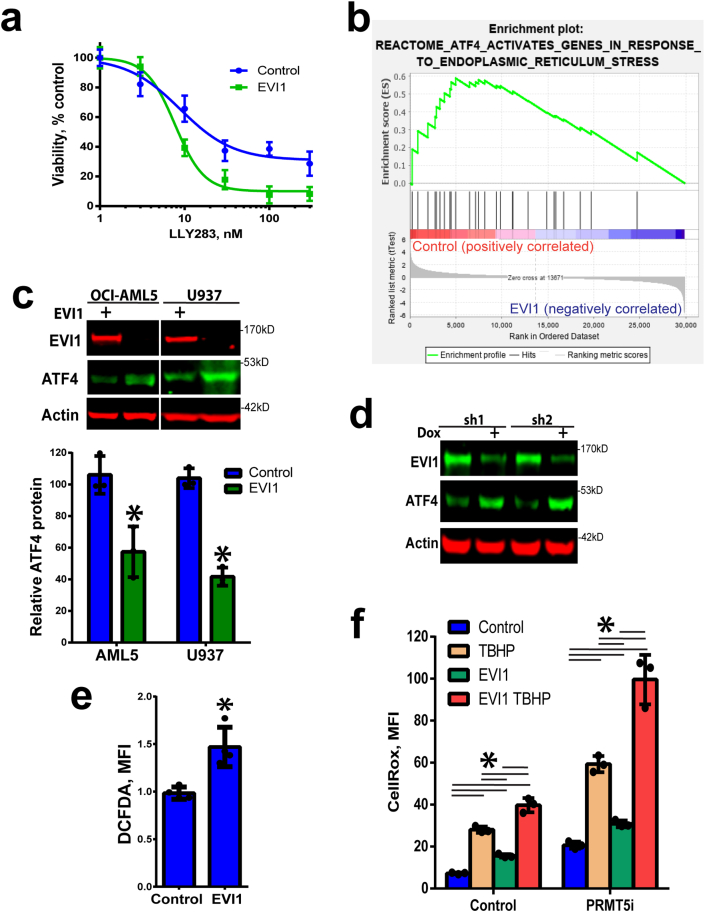
Fig. 6.
EVI1 overexpression results in decreased ATF4 levels and sensitization to PRMT5 inhibition. a) EVI1 overexpression in OCI-AML5 cells sensitizes to PRMT5 inhibition. Cell viability was assessed by resazurin assay after 5 days (N = 3, means ± SEM). b) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of EVI1 overexpressing cells (GSE34729) indicates significantly decreased enrichment for the ATF4 signature (negative correlation between EVI1 and ATF4 signatures NES = 1.67, p = 0.01). c) EVI1 overexpression leads to lower ATF4 protein levels in U937 and OCI-AML5 cells (no endogenous EVI1 expression), quantitation below (N = 3, *p < 0.05, means ± SD). d) EVI1 knockdown results in increased ATF4 levels in UCSD-AML-1 cells (EVI1-high). Dox indicates doxycycline induction of shRNA (2 days). e) Increased oxidative stress in U937 cells overexpressing EVI1 (N = 4, means ± SD, *p < 0.05). f) Increased oxidative stress in AML5 cells overexpressing EVI1 is potentiated by PRMT5 inhibition (LLY283, 100 nM, 4 days) and TBHP (200 μM, 2 h), N = 3, means ± SD, *p < 0.05 two-way ANOVA, Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test.