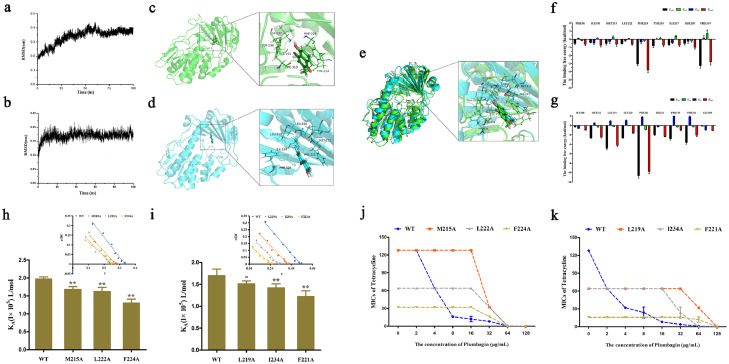
Figure 5.
Determination of the binding model of plumbagin with Tet(X3)/Tet(X4). RMSD values of the Tet(X3)-plumbagin (a) and Tet(X4)-plumbagin (b) complex during the simulation. Three-dimensional (3D) structure determination of Tet(X3) (green color) (c) or Tet(X4) (blue color) (d) with plumbagin by molecular modeling analysis. (e) Overlapping 3D structures of Tet(X3)/plumbagin and Tet(X4)/plumbagin with similar binding sites. Decomposition of the binding energy on a per-residue basis in the binding sites of Tet(X3) (f) or Tet(X4) (g) with plumbagin. The binding constants (KA) of plumbagin with Tet(X3) and its mutants (h), Tet(X4) and its mutants (i). Further, the synergistic activity of plumbagin with tetracyclines for the bacteria harbouring Tet(X3) mutants (Tet(X3)-M215A, Tet(X3)-L222A and Tet(X3)-F224A) (j) and Tet(X4) mutants (Tet(X4)-L219A, Tet(X4)-I234A and Tet(X4)-F221A) (k) were significantly decreased compared with the bacteria carrying WT-Tet(X).