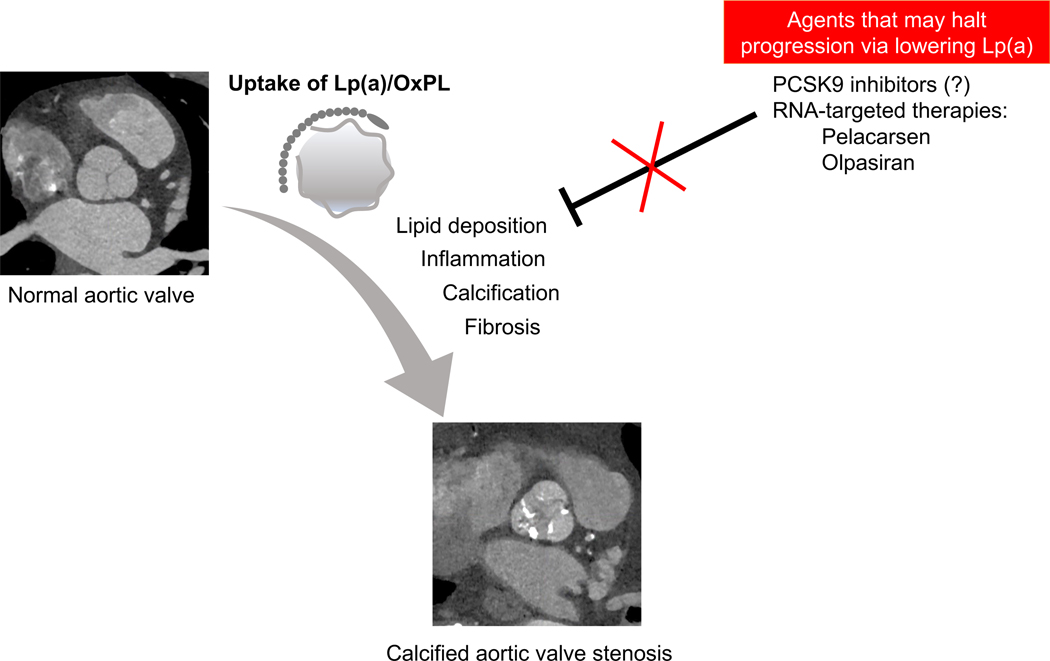
Figure 1.
Lipoprotein (a) mediates the progression of calcific aortic valvular disease. Upon endothelial damage, lipoprotein(a) and oxidized phospholipids (OxPL) accumulate within the valvular tissue, driving a feed-forward cycle of inflammation, calcification, and fibrosis. This ultimately results in calcified aortic valve stenosis. Currently, there are no approved medical therapies for aortic stenosis. However, emerging therapies to target Lp(a), including PCSK9 inhibitors and RNA-based therapeutics, may halt disease progression in aortic stenosis.