Figure 1. Hepatic expression of PAPSS2 decreases in APAP-induced hepatotoxicity and acute liver failure in patients and mice.
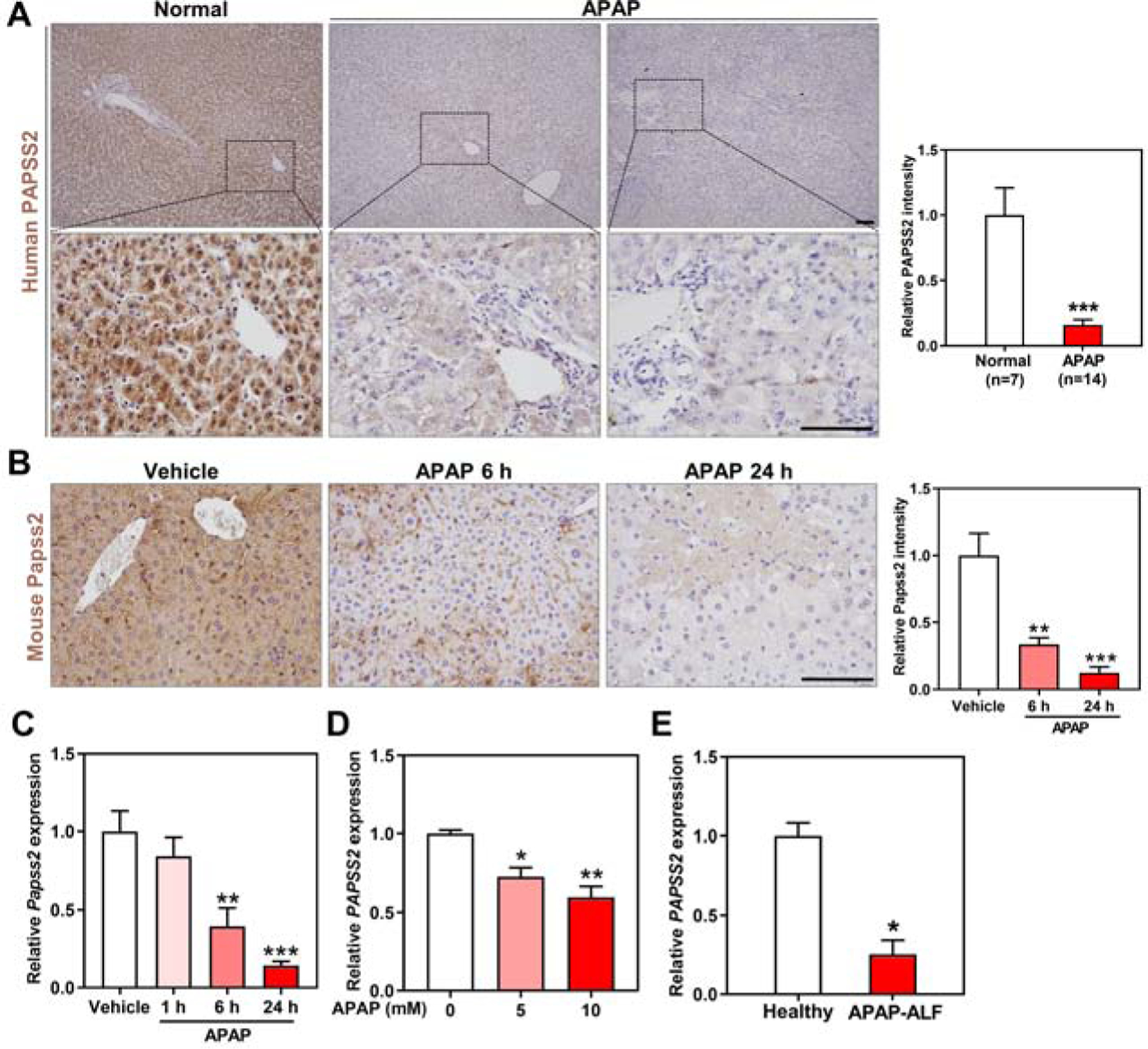
(A) Representative IHC staining of PAPSS2 in human liver sections derived from normal subjects or APAP overdose patients undergone liver transplantations. Shown on the right are the quantifications of relative PAPSS2 signals. Scale bars: 100 μm. (B) Representative IHC staining of Papss2 in livers of WT mice treated with vehicle or APAP (200 mg/kg) for indicated amount of time. Shown on the right are the quantifications of relative Papss2 signals. Scale bars: 100 μm. (C) Relative Papss2 mRNA expression in the livers of vehicle- and APAP-treated mice. (n=4–6). (D) Relative PAPSS2 mRNA expression in human primary hepatocytes treated with different doses of APAP (0, 5, 10 mM) (GSE13430). (E) PAPSS2 mRNA expression in the liver of healthy subjects and APAP-induced ALF patients (GSE74000). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .01, compared to the indicated controls. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
