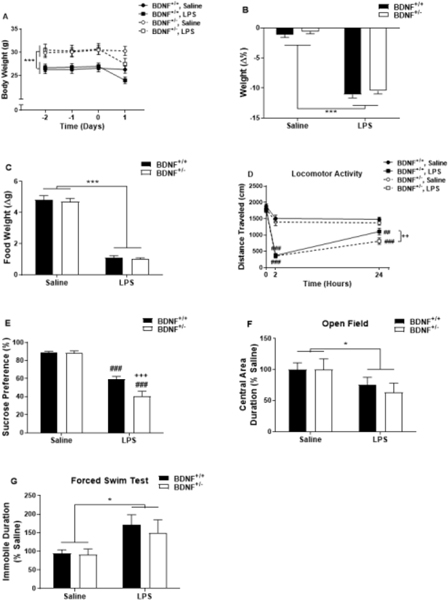
Figure 1.
BDNF deficient mice have a similar LPS-induced sickness response as WT mice but are more susceptible to the locomotor reducing effects and sucrose preference behavioral response of LPS. (A and B) Body weight was recorded prior to and following peripheral LPS administration. LPS induced a reduction in body weight in the 24h following injections in both genotypes (BDNF+/+ and BDNF+/−). (C) Food weight was also recorded, and a reduction was induced in both genotypes following LPS treatment. (D) Locomotor activity (distance traveled in an open field) was recorded for 5 minutes prior to, 2h- and 24h-post LPS treatment. Data represent sample means ± SEM and were analyzed using a two- or three-way ANOVA followed by the Holm-Sidak method for pairwise multiple comparisons. (E) After training, BDNF+/− and BDNF+/+ mice were subjected to a two-bottle (1% sucrose and water) preference test for 24h following injections. Following LPS administration, activity in the open field (OF) was assessed over a five minute period. Duration spent in the center of the arena was assessed (F, represented as % saline). (F) Duration spent immobile (represented as % saline) was assessed in the forced swim test (FST) at 24h post injections in BDNF+/− and BDNF+/+ mice. n = 5–23 mice/group.
* = main effect (treatment or genotype)
# = post-hoc comparison between saline and LPS within the same genotype (BDNF+/+ or BDNF+/−)
+ = post-hoc comparison between BDNF+/+ and BDNF+/− with the same treatment (saline or LPS)
*,+,# p<0.05–0.01 **,++,## p<0.01–0.001 ***,+++,###p<0.001