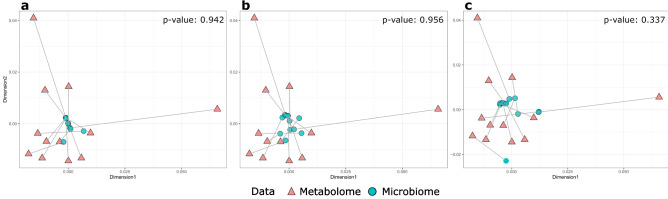
Fig. 5.
Procrustes analysis of the association between the urine metabolome and microbiome composition of cats. Only samples that passed the rarefaction curve analysis of microbiome data (i.e. > 500 16S rRNA sequences retained) were included (n = 12). The MDS ordination of metabolome data was based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity, and the ordination of microbiome data was based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity (a), unweighted Unifrac (b), and weighted Unifrac (c). One of the two ordinations were uniformly scaled and rotated until the squared differences between them were minimized, followed by the procrustean randomization test to assess the correlation between the two ordinations. Samples from the same cats are connected by a line, with orange triangles and blue circles representing samples positioned by metabolome and microbiome composition, respectively. The result of this analysis suggested no statistical evidence for the association between metabolome and microbiome composition