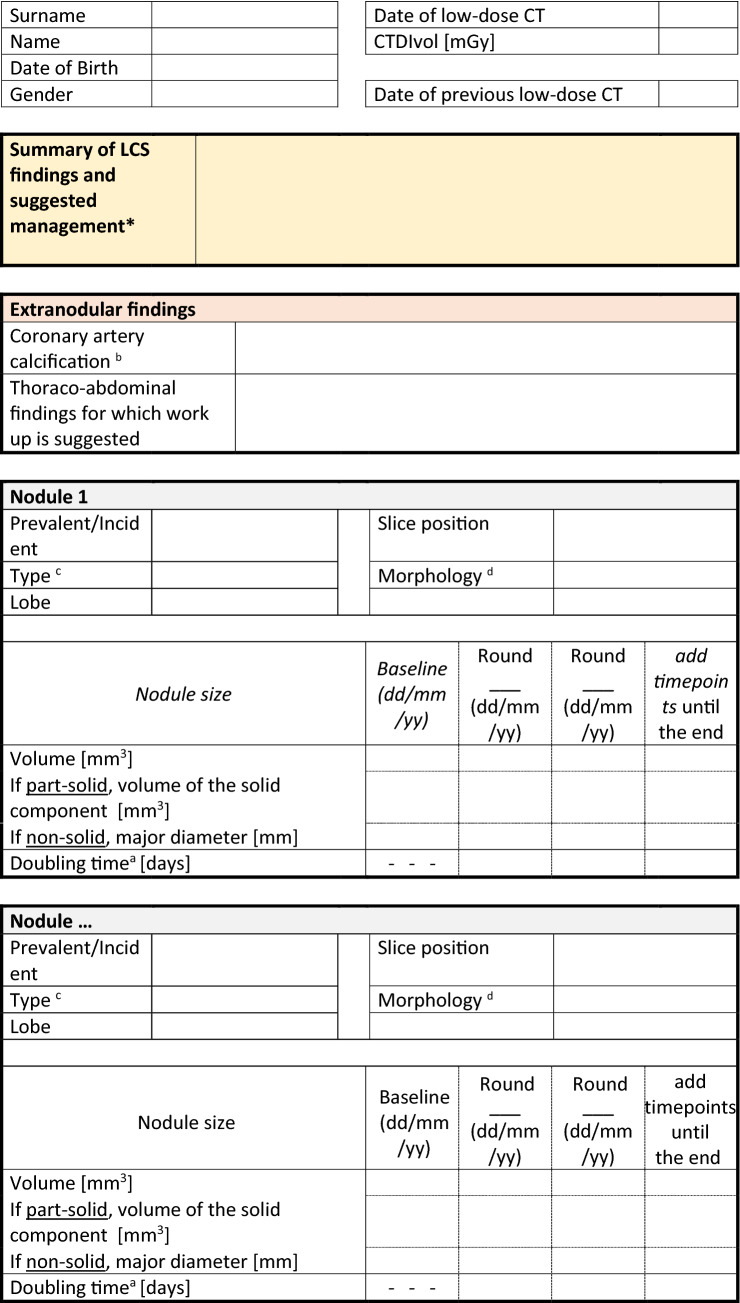
Table 3.
Structured report for LDCT in LCS (
modified from www.esti.org) with links for computation of the risk of malignancy of a nodule at baseline (Brock methods)* and of the growth at subsequent low-dose CT examinationsa
*The Brock model calculator is available online from several certified resources, for instance the “PN Risk Calculator” form the British Thoracic Society, either diameter or volume can be used (https://www.brit-thoracic.org.uk/quality-improvement/guidelines/pulmonary-nodules/pn-risk-calculator/)
aThe volume doubling time (VDT) can be calculated with measurement of nodule volume or bit is also accepted by geometric translation of mean diameter. Noteworthy, the VDT is accepted for the specific characterization of solid nodule. The VDT is currently provided by most CADe/CADx software, moreover it is also found online, for instance the “PN Risk Calculator” della British Thoracic Society.
bCoronary artery calcifications can be assessed by semi-quantitative method (0 = absent; 1 = mild; 2 = moderate; 3 = severe) or more complex (from 0 to 12 score) visual scales (see https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.15142062 and https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10100383)
cThe type of nodule is defined according to its: solid/part-solid/non-solid/calcified
dThe morphology of nodule is found in the literature and is usually aimed to stratify risk: spiculation, perifissural nodule