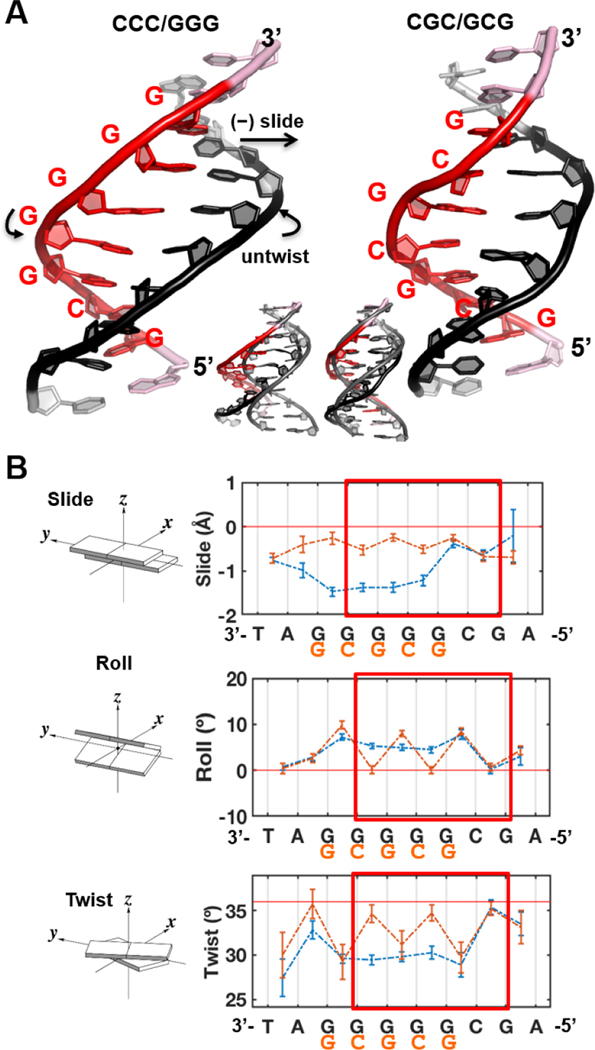
Fig.5. Intrinsic structural differences of the CCC/GGG and CGC/GCG sequences.
(A) Best representative structures. Overlay with a B-DNA model is shown in the inset. (B) The DNA sequences had prominent impacts on the helix parameters, slide, roll and twist. See Figure S10 for the other parameters, shift, rise and tilt. Illustrations of the base pair step parameters are adapted from 3DNA [109]. The standard deviations of the block averaged means [110, 111] for the parameter values are shown. The twist angle is 36º per step for ideal B-DNA. Note that the sequence labels are from 3’ to 5’. The regions boxed red are centered around the putative ‘open’ site and the end base pairs of the 6-mer regions were used to calculate the (un)twist angle upon the DNA’s initial binding with Rad4.