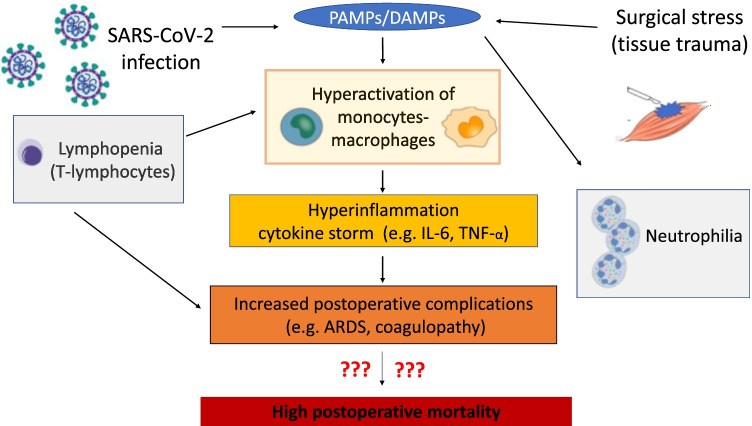
Fig. 1.
Common immunomodulatory effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection and surgical therapy on postoperative mortality. Both SARS-CoV-2 infection and surgical therapy lead to hyperactivation of macrophages through tissue damage of various causes, which first leads to local hyperinflammation. In the following course, a systemic cytokine storm may occur. In this line, lymphopenia and neutrophilia are induced. These SARS-CoV-2 driven effects on the immune system negatively influence on postoperative immune competence of patients and lead to severe postoperative complications such as ARDS, sepsis and thromboembolism. The question now concerns the impact of perioperative SARS-CoV-2 infection on postoperative mortality. ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; PAMPS, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPS, damage-associated molecular patterns; IL-6, interleukin-6, TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor-α (modified from [75]; Icons from [76, 77])