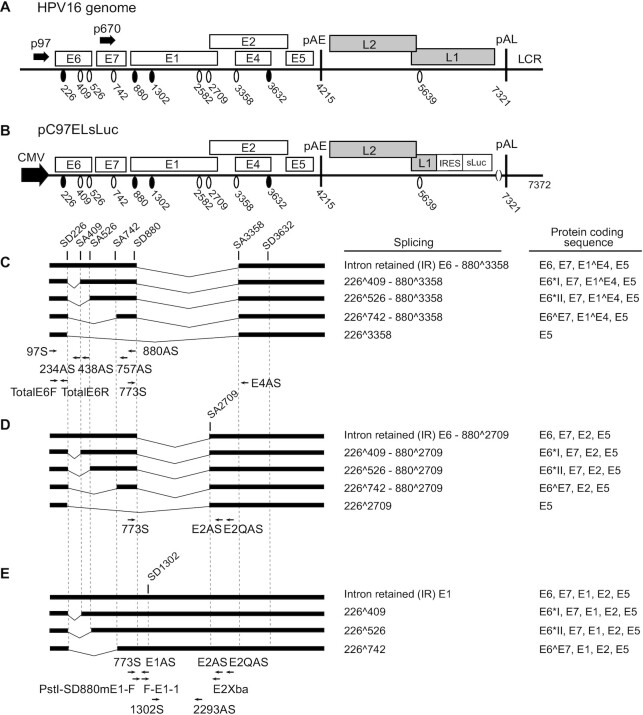
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the HPV16 genome, HPV16 subgenomic plasmid pC97ELsLuc and representative HPV16 mRNAs. (A) Linearized HPV16 genome (numbers refer to the HPV16 reference strain GeneBank: K02718.1). Early and late genes are indicated. P97: HPV16 early promoter. P670: HPV16 late promoter. Black oval: splice donor. White oval: splice acceptor. pAE: HPV16 early polyadenylation site. pAL: HPV16 late polyadenylation site. LCR: HPV16 long control region. (B) HPV16 subgenomic plasmid pC97ELsLuc encodes all HPV16 genes. HPV16 early promoter p97 was replaced by human cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter (CMV). Secreted luciferase (sLuc) gene was integrated in the L1 gene following the poliovirus 2A internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) sequence. (C–E) Schematic structures of HPV16 early transcripts produced from pC97ELsLuc. Splicing at SD226 occurs independently of splicing at the downstream SD880 and generates splice variants in the E6E7-coding region concomitantly with alternative splicing from SD880, i.e. E4 (880∧3358) (C), E2 (880∧2709) (D) or mRNAs unspliced at SD880 (E). The protein coding sequences present on each mRNA are indicated to the right. Arrows: Annealing positions of HPV16 RT-PCR primers. Primer sequences are available in Supplementary Table S1.