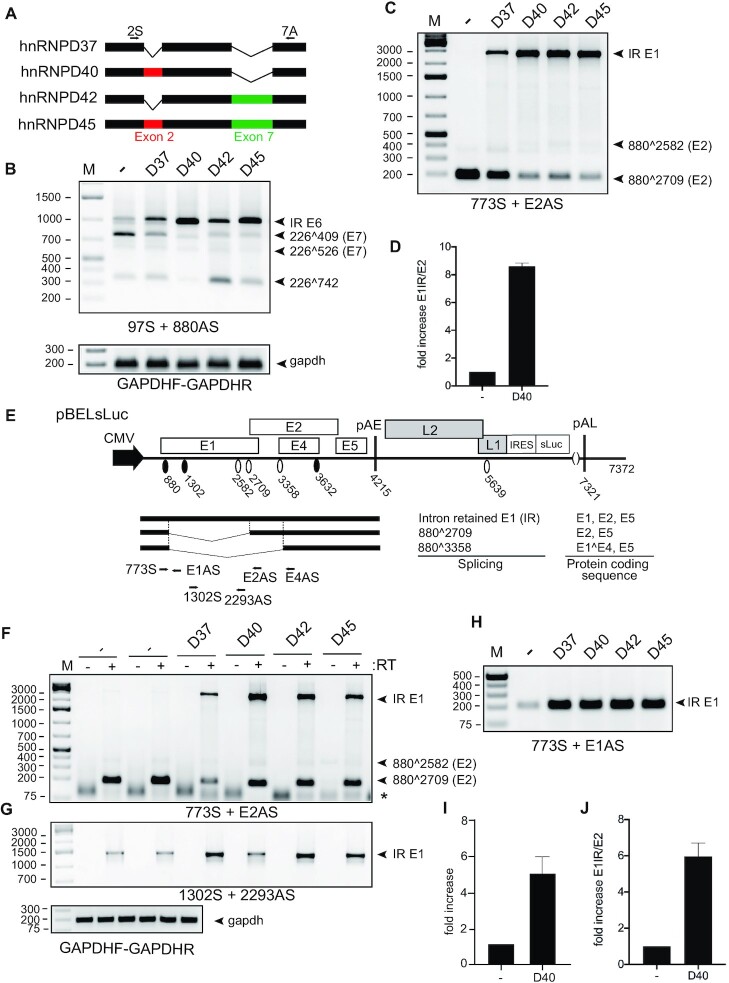
Figure 3.
hnRNP D40 enhanced the production of intron-retained E6 and E1 mRNA more potently than the other hnRNP D isoforms. (A) Schematic structures of the hnRNP D protein isoforms. Each isoform differs by the inclusion of Exon 2 and/or Exon 7, respectively. Arrows: Primers’ position used for Supplementary Figure S1F. (B and C) Effect of indicated hnRNP D isoforms on HPV16 alternative mRNA splicing was investigated by HPV16 RT-PCR on RNA extracted from HeLa cells transfected with pC97ELsLuc in the absence or presence of plasmids expressing either of the hnRNP D isoforms. HPV16 RT-PCR primer pairs: (B) 97S+880AS and (C) 773S+E2AS. (D) RT-qPCR to quantitate intron-retained E1 mRNAs and spliced E2 mRNAs from pC97ELsLuc in the absence of presence of hnRNP D40 was performed. Fold change of intron-retained E1 mRNAs over spliced E2 mRNAs is shown. (E) Schematic representation of HPV16 subgenomic plasmid pBELsLuc that encodes all HPV16 genes except E6 and E7 and is driven by the CMV promoter. HPV16 mRNAs polyadenylated at pAE are shown below pBELsLuc. Arrows: Annealing positions of HPV16 RT-PCR primers. Primer sequences are available in Supplementary Table S1. (F–H) Effect of indicated hnRNP D isoforms on HPV16 mRNA splicing was further investigated with plasmid pBELsLuc. pBELsLuc was cotransfected with indicated hnRNP D isoform expressing plasmids into HeLa cells. Total RNA was extracted and subjected to RT-PCR using different HPV16 RT-PCR primers pairs. RT-PCR was performed in the absence (−) or presence (+) of reverse transcriptase: (F) 773S+E2AS, (G) 1302S+2293AS and (H) 773S+E1AS. Only RT (+) samples for gapdh RT-PCR are shown. (I) RT-qPCR with primer pairs 773S+E1AS, normalized to GAPDH levels. (J) RT-qPCR to quantitate intron-retained E1 mRNAs over spliced E2 mRNAs from pBELsLuc in the absence or presence of hnRNP D40. Fold change of intron-retained E1 mRNAs over spliced E2 mRNAs is shown.