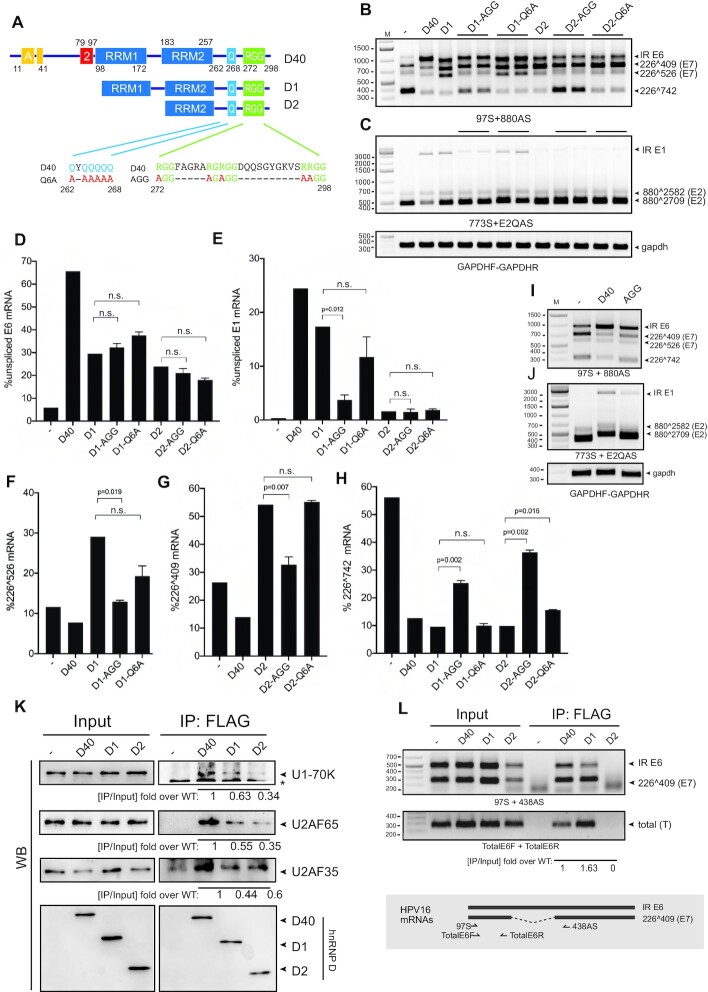
Figure 5.
hnRNP D40 C-terminus contributes to HPV16 mRNA splicing control differently from its N-terminus. (A) Schematic structures of hnRNP D40 and various hnRNP D40 mutants with N-terminal deletions and C-terminal amino acid substitutions. Amino acid substitutions in the Q-rich region or the RG/RGG-motif region are indicated. Q: Glutamine, A: Alanine and R: Arginine. ‘- ’ indicates wild-type sequence. (B and C) Effect of hnRNP D40 or hnRNP D40 mutants on HPV16 E6/E7 mRNA splicing (B) or E1/E2 mRNA splicing (C) was monitored by RT-PCR with indicated primer pairs. (D–H) Percentage of an indicated HPV16 mRNA splice variant among all spliced isoforms of HPV16 E6/E7 or E1/E2 mRNAs was quantitated from (B) and (C) as described in Figure 2D and E: (D) percentage intron-retained E6 mRNAs, (E) percentage intron-retained E1 mRNAs, (F) percentage 226∧409 mRNAs, (G) percentage 226∧526 mRNAs and (H) percentage 226∧742 mRNAs. Student’s t-test was executed and obtained P values were displayed. n.s., no significance. (I and J) Effects of amino acid substitutions in the RG/RGG region of full-length hnRNP D40 on HPV16 mRNA splicing was monitored by HPV16 RT-PCR as described in (B). (K) Interactions between hnRNP D40 and cellular spliceosome factors U1-70K, U2AF65 and U2AF35 were investigated by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay. Indicated FLAG-tagged, wild-type or mutant hnRNP D40 expression plasmid was transfected into HeLa cells. Whole cell extracts were subjected to IP by anti-FLAG antibody to purify the FLAG-protein interactome complex, followed by western blotting to detect the presence of endogenous cellular spliceosome factors in the complex. Band intensity was quantitated and IP efficiency was calculated as IP band intensity over corresponding Input band intensity. Fold change over WT D40 of IP efficiency is shown under each western blot image. (L) Interactions between hnRNP D40 and HPV16 mRNAs were investigated by UV-crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (CLIP) assay. HPV16 subgenomic plasmid pC97ELsLuc was cotransfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type or mutant hnRNP D40 expression plasmid into HeLa cells. UV-crosslinked whole cell extracts were subjected to IP by anti-FLAG antibody followed by extraction of RNA from the FLAG-protein interactome complex and RT-PCR using HPV16-specific RT-PCR primers, 97S+438AS or TotalE6F+TotalE6R. The schematic depiction of the location of the HPV16-specific RT-PCR primers is shown below the gel image. Fold change of CLIP efficiency of wild-type and mutant hnRNP D40s over wild-type D40 was calculated as described in (K).