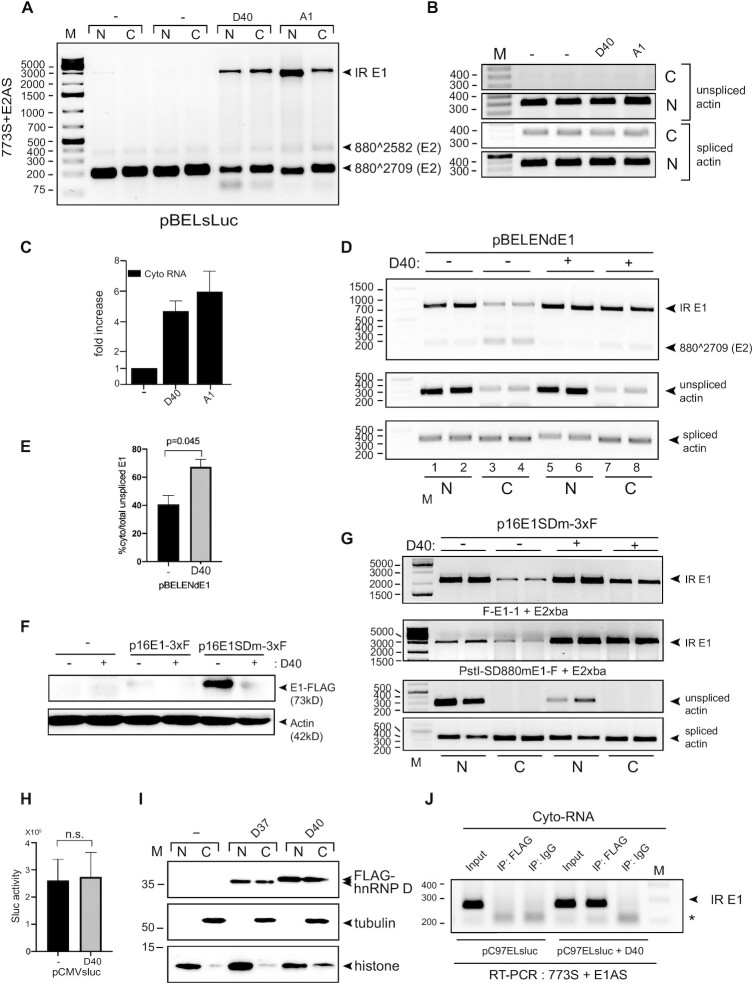
Figure 7.
hnRNP D40 upregulated levels of HPV16 intron-retained E1 mRNAs in the cytoplasm and interacts with these mRNAs in the cytoplasmic fraction. (A) HeLa cells were transfected with pBELsluc plasmid in the absence (−) or presence of plasmids expressing either hnRNP D40 or hnRNP A1. Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions were prepared from the transfected cells and RNA was extracted and subjected to HPV16-specific RT-PCR using primer pair 773S+E2AS. (B) Cellular fractionation was validated by analysis by RT-PCR of unspliced and spliced actin mRNAs. (C) Levels of HPV16 intron-retained E1 mRNAs in the cytoplasmic fraction was determined by RT-PCR with primers 773S+E1AS. Quantification of electrophoresed RT-PCR products were performed as described and normalized to RT-PCR products representing cytoplasmic spliced actin mRNA. Fold over control (−) is shown. (D) Effect hnRNP D40 on subcellular localization of HPV16 intron-retained E1 mRNAs and spliced E2 mRNAs produced from HPV16 subgenomic plasmid pBELENdE1 (for schematic representation of pBELENdE1, see Supplementary Figure S7C). pBELENdE1 was transfected into HeLa cells in the absence (−) or presence (+) of hnRNP D40 plasmid. RT-PCR was performed on nuclear or cytoplasmic RNA using HPV16-specific primers pair 773S+E2Xba that detects HPV16 intron-retained E1 mRNAs as well as spliced mRNAs (880∧2709). (E) Percentage cytoplasmic intron-retained HPV16 E1 mRNAs over a total sum of nuclear and cytoplasmic intron-retained E1 mRNAs in absence (−) or presence of hnRNP D40 from (D). (F) Effect of hnRNP D40 on HPV16 E1 protein levels was determined by western blotting on extracts form HeLa cells transfected with HPV16 E1-FLAG expressing plasmid p16E1-3xF (wild type) or p16E1SDm-3xF (harboring mutations at splice donors SD880 and SD1302 in the E1 gene thereby abolishing E2 mRNA splicing), in the absence (−) or presence (+) of hnRNP D40 expressing plasmid. Western blotting using anti-FLAG antibody (M2). (G) The levels of HPV16 intron-retained E1 mRNAs produced by p16E1SDm-3xF in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, in the absence (−) or presence (+) of hnRNP D40 expression plasmid, was determined by HPV16-specific RT-PCR primers primer pairs F-E1-1+E2Xba and PstI-SD880mE1-F+E2Xba (primer positions are displayed in Supplementary Figure S7). (H) Overexpression of hnRNP D40 does not affect production of sLuc from a CMV-promoter driven sLuc gene. (I) HeLa cells were transfected with indicated, FLAG-tagged hnRNP D expression plasmids. Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were subjected to Western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody or anti-tubulin or anti-histone antibody to control for subcellular fractionation. (J) Association between HPV16 E1 mRNAs and hnRNP D40 protein in the cytoplasm demonstrated by CLIP assay on cytoplasmic extracts from HeLa cells transfected with HPV16 subgenomic plasmid pC97ELsLuc in the absence or presence of FLAG-hnRNP D40 expressing plasmid. Cytoplasmic extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody to purify FLAG-hnRNP D40: RNA complexes. RNA in the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex was extracted and subjected to RT-PCR using primers 773S and E1AS that specifically detect HPV16 intron-retained E1 mRNAs.