Figure 1.
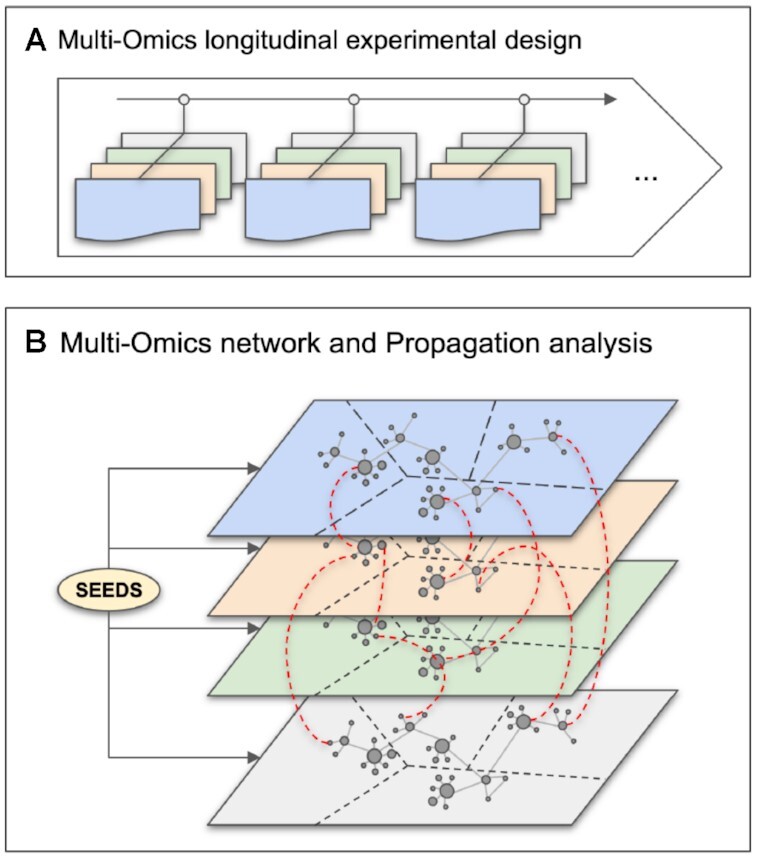
Overview of the proposed approach. (A) Description of the experimental design: the same biological material is sampled at several time points across several omic layers indicated in different colors. Each omic data is normalised using both platform-specific and time-specific normalisation steps. (B) Multi-Omics Network is built using both inference-based and knowledge-based methods to connect intra- and cross-layered biological features or molecules (mRNA, proteins, metabolites). Measured molecules are clustered into groups of similar expression profiles over time and corresponding nodes formed kinetic sub-networks. Over-representation analysis is performed to add an extra layer of functional annotation. Propagation analysis is performed on specific nodes of interest, called seeds (biological function, gene, protein, metabolite, etc.) to identify closely related molecules.
