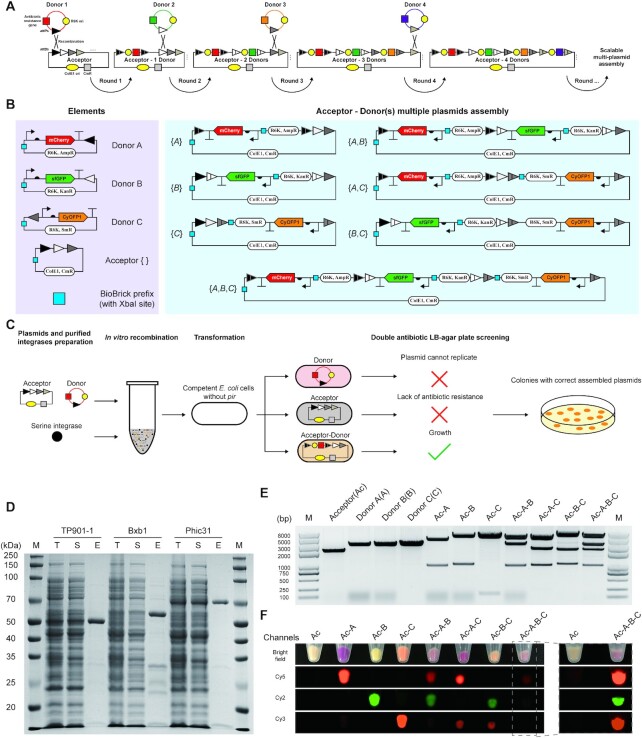
Figure 4.
SYMBIOSIS enables in vitro multiple plasmid assembly. (A) Principle and design of scalable ‘acceptor–donor(s)’ assembly. In the first round, the ‘donor 1’ plasmid is integrated into the ‘acceptor’ backbone by one serine integrase, forming a combined ‘acceptor–1 donor’, which can serve as a new ‘acceptor’ in the next round of assembly. The ‘acceptor’ plasmid has different attB sites, which are paired to their cognate attP sites in the ‘donor’ plasmids. ‘Donor’ plasmids use the same R6K ori and each one has its own unique antibiotic resistance gene, allowing for the subsequent plasmid screening. In addition, each ‘donor’ plasmid carries a target biobrick (e.g. gene coding sequence) for desired application. (B) A paradigm of in vitro SYMBIOSIS for multiple plasmid assembly. Left, three ‘donor’ plasmids (pFB63–pFB65) harboring three fluorescent proteins, respectively, and one ‘acceptor’ (pFB62). Right, seven composite plasmids after assembly (pFB66–pFB72). The details of these plasmids are shown in Supplementary Table S5. (C) Schematic workflow of in vitro SYMBIOSIS. (D) SDS-PAGE analysis of three purified serine integrases (TP901-1: 56.5 kDa; Bxb1: 57.2 kDa; and Phic31: 67.9 kDa). T, cell lysate; S, supernatant fraction; E, purified enzyme. (E) DNA fragment sizes of the ‘acceptor’, ‘donors’ and assembled plasmids after XbaI digestion. All expected bands are observed on the agarose gel (from left to right, pFB62: 2218 bp; pFB63: 3284 bp; pFB64: 3243 bp; pFB65: 3276 bp; pFB66: 4516 + 986 bp; pFB67: 4410 + 1051 bp; pFB68: 5341 + 153 bp; pFB69: 4410 + 3349 + 986 bp; pFB70: 5341 + 2451 + 986 bp; pFB71: 5341 + 2345 + 1051 bp; pFB72: 5341 + 3349 + 2345 + 986 bp). (F) Orthogonal fluorescence detection of E. coli with assembled plasmids. Four channels (bright field, Cy5, Cy2 and Cy3) are used to detect the fluorescence of all cell pellet samples. For E. coli containing the triple assembled plasmid (pFB72, Ac-A-B-C), the pellet sample is also independently detected with the negative control of ‘acceptor’ (pFB62, Ac) to show clear fluorescent signals. All samples are repeated by three biological replicates with similar results.