Figure 1.
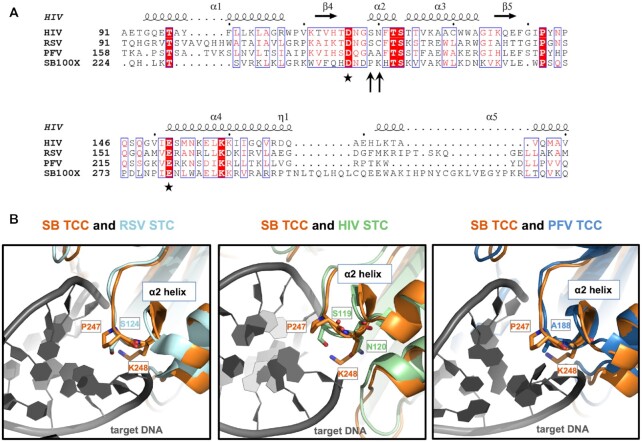
Sequence alignment and structural superposition identify P247 and K248 in the Sleeping Beauty transposase as potential equivalents of amino acids in retroviral integrases responsible for interactions with target DNA. (A) Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of segments of retroviral INs and the SB transposase. The alignment was generated by CLUSTALW and then used to highlight secondary structures of HIV IN (based on PDB ID: 1BIS) with ESPript 3.0 (100). Accordingly, the numbering of alpha helices and beta strands corresponds to HIV IN. The second D and the E residues of the catalytic DDE triads are marked with asterisks. P247 and K248 of SB (arrows) are located three and four amino acids downstream of the second D, respectively, in a region corresponding to the α2 helix of the retroviral INs. (B) Superposition of the SB TCC model with structures of retroviral intasomes. S124 of RSV STC [light blue, PDB ID: 5EJK (22)], S119 of HIV-1 STC [green, PDB ID: 5U1C (54)] and A188 of PFV TCC [dark blue, PDB ID: 3OS1 (15)] all overlay with P247 of the SB transposase (orange). SB’s K248 and HIV IN’s equivalent N120, both situated within the conserved α2 helix, are also displayed. The target DNA is depicted in dark gray.