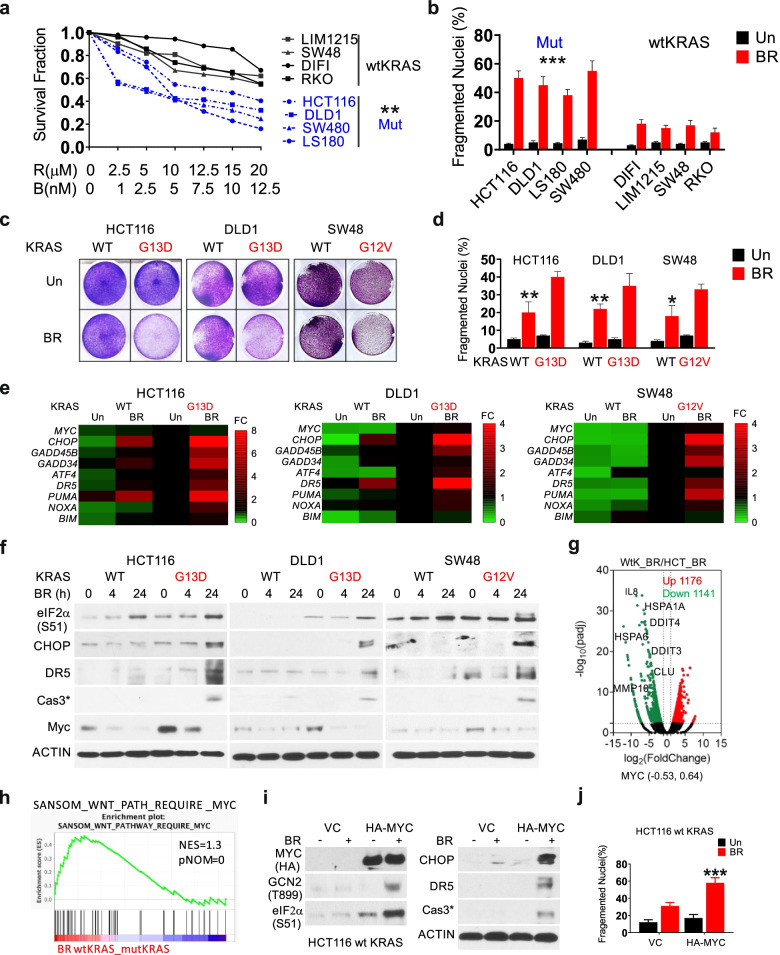
Fig. 4.
The BR combination induces mutant KRAS-selective stress hyperactivation and cell death. CRC cells with either WT or mutant KRAS were treated with vehicle (Un), or the Bortezomib (B) and Everolimus (R) combination (BR, 5 nM and 10 µM, or as specified). a Dose response of 8 cell lines at 48 h was assessed by MTS assay. Dotted (blue) or solid lines represented cells with MUT or wtKRAS. b Apoptosis at 48 h was analyzed by nuclear fragmentation assay. c Attached cells at 48 h were visualized by crystal violet staining. d Apoptosis at 48 h was analyzed by nuclear fragmentation assay. e qRT-PCR analysis of indicated genes at 24 h visualized by heatmap. The expression was normalized to untreated isogenic mutant KRAS cells (1). f Western blotting of indicated proteins at 0, 4 and 24 h. g DEGs (FC ≥ 2, p < 0.005) in BR-treated WT vs. mut KRAS HCT 116 cells at 24 h visualized by volcano plot. Selected down-regulated genes (green) in WT KRAS cells are shown. h GSEA of differential genes in the indicate pair (C2 dataset). The indicated gene set is shown with NES and corresponding p-value. i Cells were transfected with either empty vector (VC) or HA-MYC plasmid for 24 h, replated for 24 h, and treated with BR. Western blotting of indicated proteins at 24 h, and j apoptosis at 48 h analyzed by nuclear fragmentation assay. a, b, d, j, values are mean + s.d. (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 (Student’s t-test, two tailed). WT vs. mut KRAS BR group or cell line, or VC vs. HA-MYC