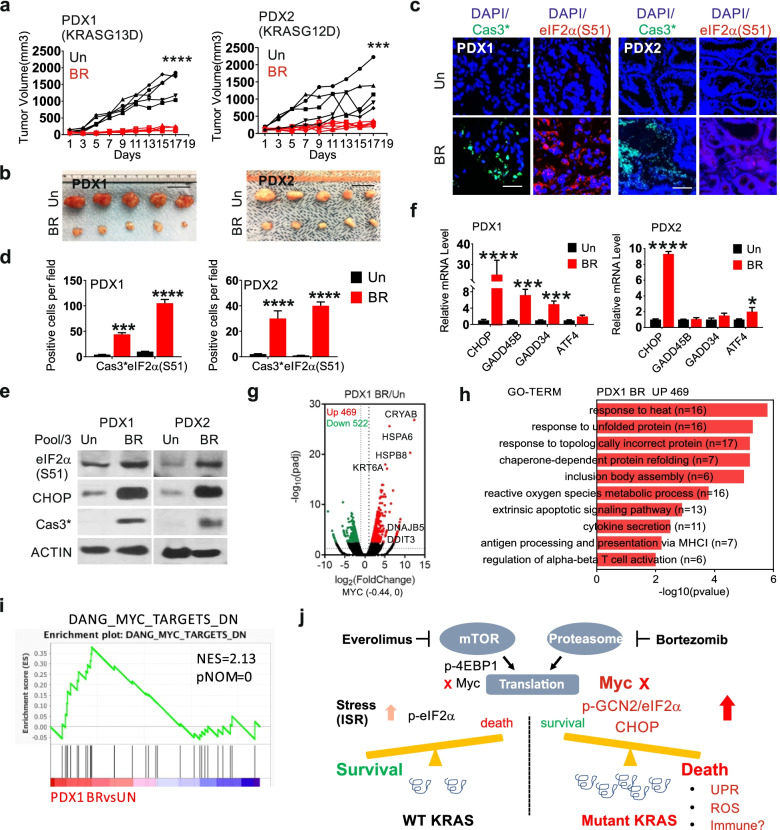
Fig. 6.
The BR combination kills mutant KRAS MSS CRC PDXs. NSG were randomized into control and treatment groups when average PDX volume reached around 100 mm3. Mice were treated with vehicle (Un), or the combination of Everolimus (oral gavage, 10 mg/kg) and Bortezomib (i.p., 0.5 mg/kg) (BR) every other day starting day 1. Tumors were harvested for analysis. a Individual tumor volume was calculated and plotted (n = 5) with b representative images on day 17. Scale Bar = 2 cm. c Representative cleaved caspase 3 and p-eIF2α IF with DAPI counterstain (blue) on day 4. Scale Bar = 100 µM. d Quantification of cleaved-caspase 3 and p-eIF2α IF as (c) in 3 randomly chosen 400X fields. e Western blotting of indicated proteins on day 4. N = 3 (pooled). f qRT-PCR of indicated makers on day 4. The values were normalized to Un (1). N = 3 (pooled mRNA). g BR DEGs in PDX1 on day 4 visualized by volcano plot. Upregulated (red) or down regulated (green) genes (fold ≥ 2, p < 0.005). Selected upregulated genes are shown. h Top 10 enriched non-overlapping pathways identified by GO in upregulated genes (469). i. GSEA of differential genes in PDX1 (C2 dataset). The indicated gene set is shown with NES and corresponding p-value. a, d, f, values are mean + s.d. (n = 3 or as specified). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 (Student’s t-test, two tailed). Vehicle (Un) vs. BR. j Working model. Targeting Myc-driven stress in KRAS mutated CRCs. Compared to WT KRAS CRCs, mutant KRAS CRCs show elevated basal Myc and metabolic stress. Acute ablation of Myc protein by the BR combination impairs their adaptation, leading to sustained ISR (p-GCN2/p-eIF2α/CHOP) and cell death associated with UPR, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and immune activation