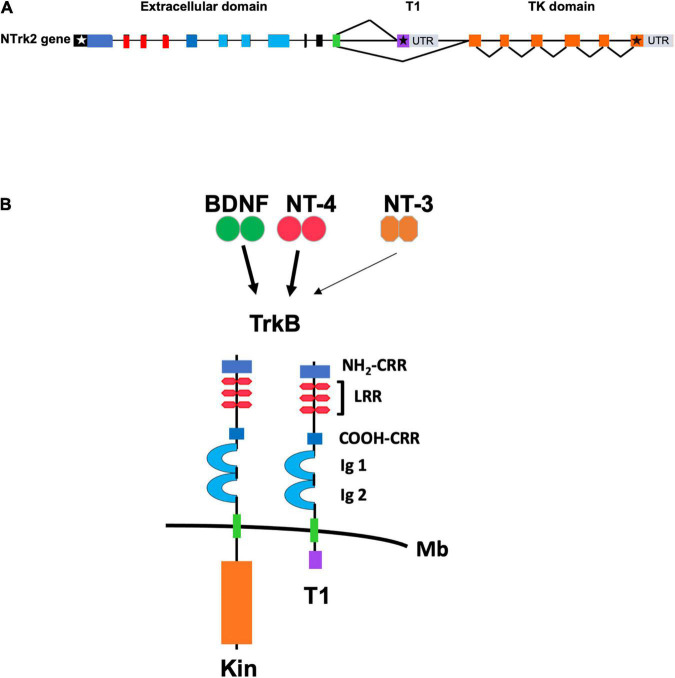
FIGURE 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the genomic structure of the murine TrkB gene. Exons are shown as boxes and introns are shown as lines. White and black stars indicate the start and stop condons, respectively. Color of exons indicate the domains of the TrkB protein isoforms shown in panel (B). Gray boxes indicate the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the TrkB transcripts. T1 and TK (Tyrosine Kinase) domain indicate the exons encoding, respectively, the TrkB.T1 and the TrkB.FL isoform that are produced by alternative splicing. (B) Schematic representation of the TrkB tyrosine kinase and TrkB.T1 isoform receptors. The extracellular TrkB protein domains include the amino (NH2-CRR) and carboxy (COOH-CRR) cysteine rich region; the leucine rich region (LRR) and the IG like, immunoglobulin like-domain (Ig1 and Ig2). The intracellular tyrosine kinase (Kin) and T1 domain are indicated below the cell membrane (Mb). BDNF and Neurotrophin-4 (NT-4) are the TrkB ligands binding with high affinity (solid arrow) whereas Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) binds to the extracellular domain with lower affinity (thin arrow).