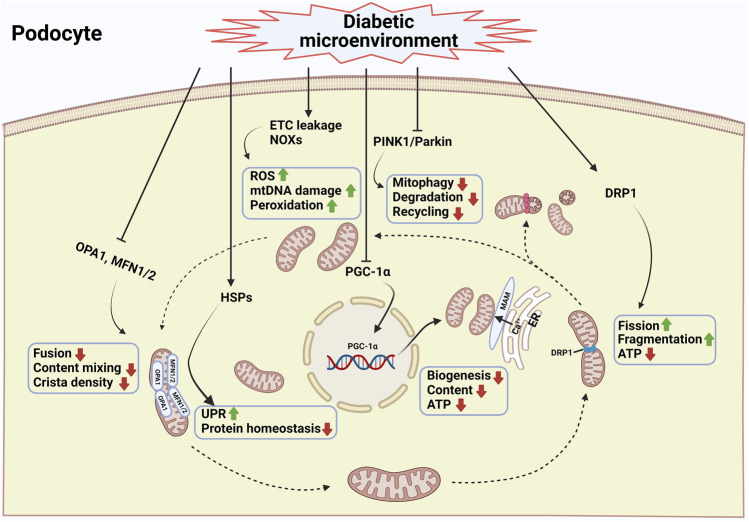
FIGURE 1.
Mitochondrial damage of podocytes during diabetic kidney disease. Mitochondria are highly dynamic organelles that respond to pathophysiologic cues by altering mitochondrial content, fusion, fission, mitophagy, and the unfolded protein response. Fission and fusion complement each other to maintain mitochondrial morphology, whereas mitophagy selectively clears damaged mitochondria from the network (Nisoli et al., 2004). Excessive mitochondrial fission combined with decreased mitochondrial fusion is a prototypical feature of podocytes in diabetic kidney disease (Wang et al., 2012; Ayanga et al., 2016; Qin et al., 2019; Audzeyenka et al., 2021). In addition, the inhibition of mitophagy leads to the lack of a proper mitochondrial turnover in the diabetic kidney (Li et al., 2016; Li W. et al., 2017). Another key feature of mitochondrial dysfunction of podocytes in diabetic kidney disease is the reduced efficiency of mitochondrial biogenesis (Sun et al., 2014; Li S.-Y. et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2018). Under high glucose condition, intracellular ROS production, mitochondrial DNA damage and protein and lipid peroxidation were enhanced (Tan et al., 2010; Dugan et al., 2013; Coughlan et al., 2016). In addition, mitochondrial protein homeostasis is challenging because of the continuous exposure of mitochondrial proteins to mitochondrial ROS. Mitochondria within a cell cannot exist in isolation. They interact with endoplasmic reticulum via the formation of mitochondrial-associated membranes (MAMs). The disturbance of MAMs leads to abnormal intracellular Ca2+ influx, mitochondrial damage, and apoptosis (Inoue et al., 2019). A combination of the above factors resulted in podocyte injury and the progression of diabetic kidney disease. The podocyte mitochondria in diabetic condition is illustrated schematically with blue frame and text. DRP1, dynamin-1-like protein; MFNs, mitofusin proteins 1 and 2; ETC, electron transport chain; HSPs, heat shock proteins; MAM, mitochondria associated ER membrane; NOXs, NADPH oxidases; OPA1, optic atrophy protein 1; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ coactivator-1α; PINK1, PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; UPR, unfolded protein response (Created with BioRender.com).