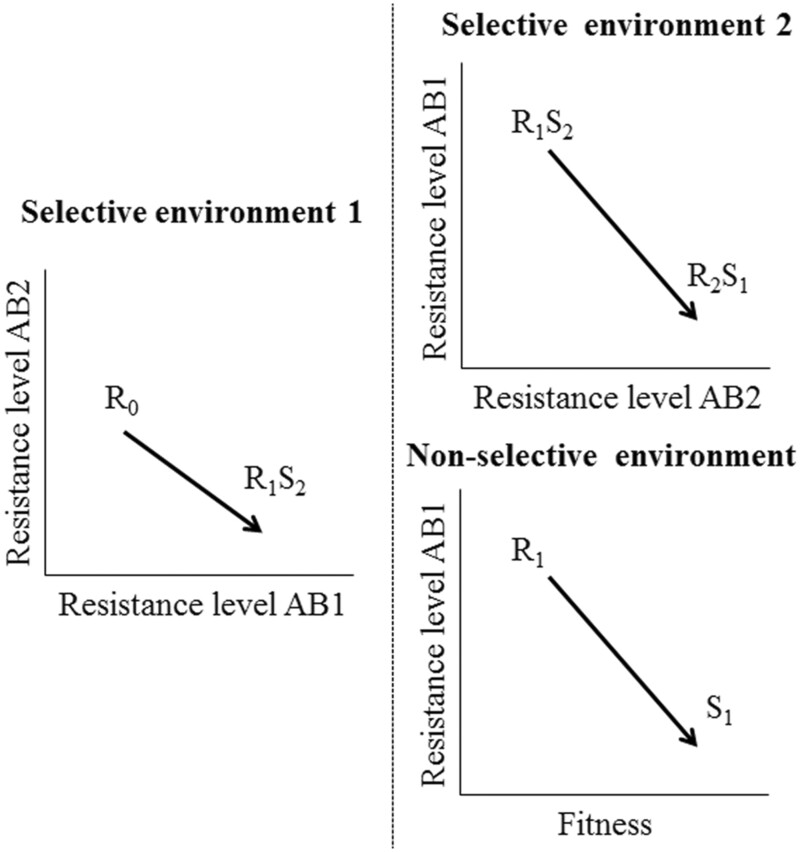
Fig. 1.
Conceptual figure representing phenotypic reversion of drug resistance. Departing from an initial AR phenotype (R0), exposure to a first antibiotic (AB1) may select resistance to that first drug (R1) and CS (S2) to a second antibiotic (AB2) (selective environment 1). After that first step, which leads to an organism resistant to the first drug and susceptible to the second antibiotic (R1S2), reversion of resistance acquired may occur in sublethal concentrations of AB2 that select resistance to this antibiotic and CS to AB1 (R2S1) (selective environment 2). This decline of resistance may also occur in antibiotic-free environments or sublethal antibiotic concentrations that do not select resistance, when fitness costs of resistance to the first drug are compensated (nonselective environment), hence moving from low fitness and resistance to AB1 (R1) to a high fitness related susceptible phenotype (S1).