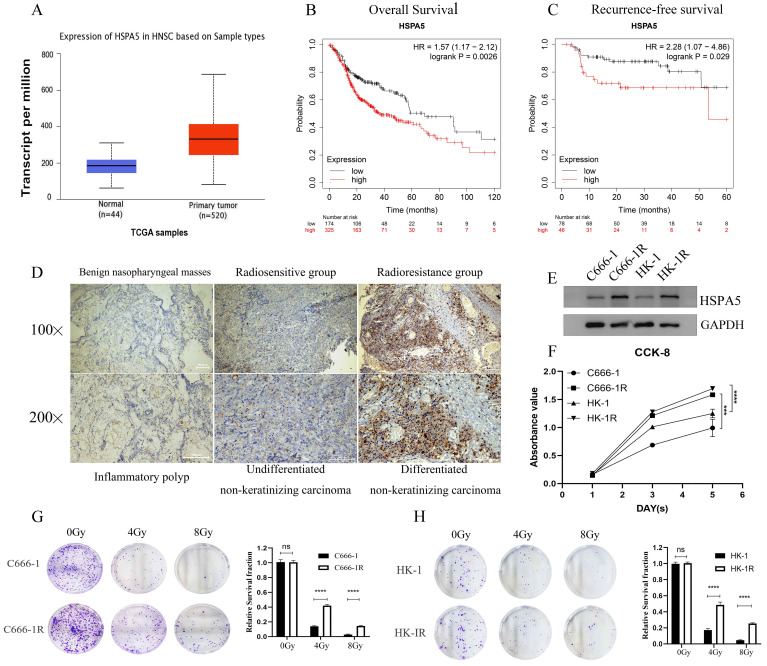
Figure 1.
HSPA5-associated radioresistance of NPC. (A) Starbase database analysis showed that the expression of HSPA5 was correlated with the occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. (B, C) Kaplan-Meier Plotter database analysis showed that the expression of HSPA5 was correlated with the prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. (D) Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to analyze the correlation between HSPA5 and radioresistance of NPC. The expression of HSPA5 was increased in NPC tissues compared to benign nasopharyngeal masses; HSPA5 was expressed more higher in the recurrent radioresistant NPC tissues than in the radiosensitivity NPC tissues. (E) Western Blot experiment verified the difference for HSPA5 higher in radioresistant NPC cells than in the parent cells. (F) The CCK-8 assay showed the difference in proliferation between the parental and constructed cell lines; and the proliferation ability of the radioresistant NPC cell lines was found to be greater. (G, H) Colony formation experiments were performed to verify the differences in colony formation ability upon treatment with radiation; and the radioresistance of C666-1R and HK-1R was significantly enhanced in comparison to the parental cell lines.