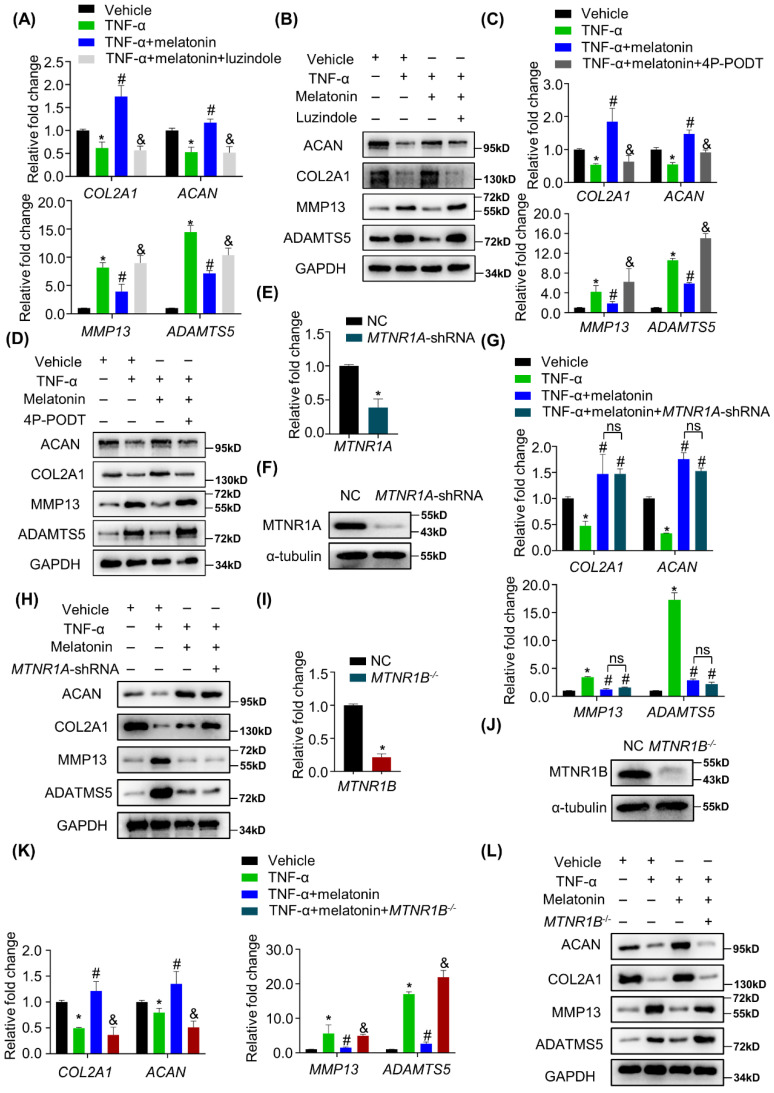
Figure 4.
Melatonin reverses TNF-α-impaired metabolic activities of NP cells via MTNR1B. RT-qPCR (A) and WB (B) analyses were performed to assess the expression of COL2A1, ACAN, MMP13, and ADAMTS5 in human NP cells with or without pretreatment of luzindole (5 μM) for 1 hour followed by treatment with vehicle (ethanol), TNF-α (10 ng/ml), and melatonin (100 μM) for 48 hours. Then, RT-qPCR (C) and WB (D) analyses were performed to assess the expression of COL2A1, ACAN, MMP13, and ADAMTS5 in human NP cells with or without pretreatment with 4P-PODT (10 μM) for 1 hour before the treatment of vehicle (ethanol), TNF-α (10 ng/ml), or melatonin (100 μM) for 48 hours. MTNR1A was silenced by lentivirus-mediated transfection of MTNR1A-shRNA in human NP cells. RT-qPCR (E) and WB (F) analyses were performed to confirm the silencing efficiency. Then, NP cells were treated with indicated treatment and the expression of anabolic and catabolic markers were detected by RT-qPCR(G) and WB(H). MTNR1B was deleted by lentivirus-mediated transfection of MTNR1B-Cas9 in NP cells, and RT-qPCR (I) and WB (J) analyses were conducted to confirm the depletion efficiency. Then, NP cells were treated with indicated treatment and the expression of anabolic and catabolic markers were detected by RT-qPCR (K) and WB (L). * means P < 0.05 compared with the vehicle group. # means P < 0.05 compared with the TNF-α group. & means P < 0.05 compared with the TNF-α and melatonin group. Ns means not significant.