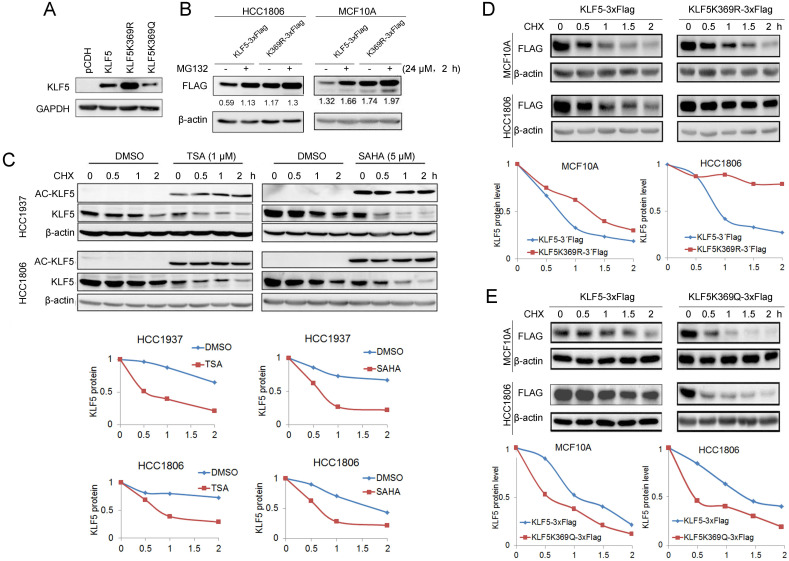
Figure 3.
KLF5 acetylation at K369 promoted its degradation. A, WT KLF5, KLF5-K369R, and KLF5-K369Q were transfected in HEK293T cells. KLF5 expression levels were detected by Western blotting. B, KLF5-K369R was more stable than WT KLF5 protein in basal-like breast epithelial cells. WT KLF5-3×Flag and KLF5-K369R-3×Flag were stably overexpressed in HCC1806 and MCF10A cells. MG132 (24 μM) was added to treat the cells for 2 h. The KLF5/β-actin band intensity ratios are labeled below the blots. C, TSA and SAHA promoted the degradation of the KLF5 protein in HCC1937 and HCC1806 cells. The cells were treated with TSA (1 µM) or SAHA (5 µM) for 24 h. Then the cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX, 50 μg/mL) for 0.5, 1, and 2 h. The cell lysates were collected for Western blotting. The quantitative results are plotted below. β-actin was used as the loading control. D, KLF5-K369R was more stable than WT KLF5 protein in basal-like breast epithelial cells. WT KLF5-3×Flag and KLF5-K369R-3×Flag were stably overexpressed in HCC1806 and MCF10A cells. The cells were treated with CHX (50 μg/mL) for 0.5, 1, and 2 h. The quantitative results are plotted below. E, KLF5-K369Q was less stable than WT KLF5 protein in basal-like breast epithelial cells. WT KLF5-3×Flag and KLF5-K369Q-3×Flag were stably overexpressed in HCC1806 and MCF10A cells. The cells were treated with CHX (50 μg/mL) for 0.5, 1, and 2 h. The quantitative results are plotted below.