FIGURE 1.
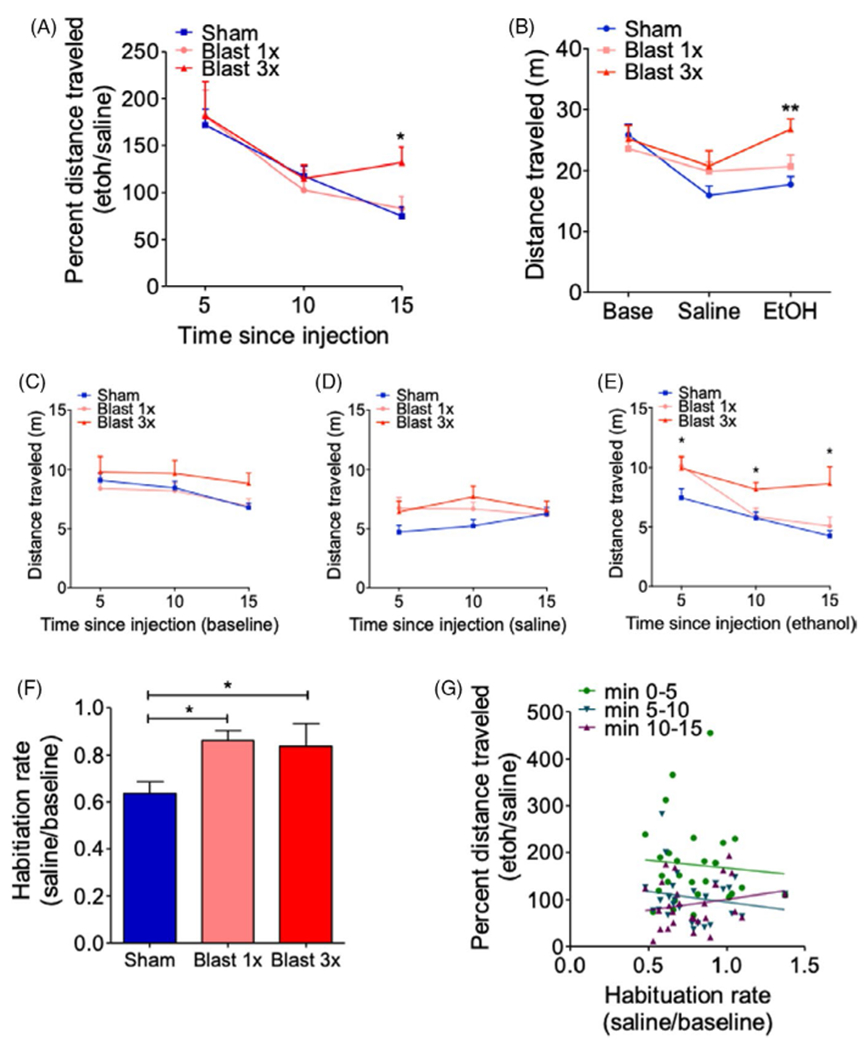
Repetitive blast exposure increases ethanol (EtOH)-induced locomotor stimulation (A) Locomotor stimulating effects of EtOH as expressed by percent distance traveled. Two-way RM ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison test. (B) Distance traveled at baseline and following saline or EtOH administration. Two-way RM ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison test. (C) Distance traveled at baseline in 5-min bins. Two-way RM ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison test. (D) Distance traveled following saline administration in 5-min bins. Two-way RM ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison test. (E) Distance traveled following EtOH administration in 5-min bins. Two-way RM ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison test. (F) Locomotor habituation. One-way ANOVA post hoc Newman–Keuls comparison test. (G) Correlation between EtOH locomotor stimulation and locomotor habituation rate. Spearman correlation. *p ≤ 0.05 **p ≤ 0.001: sham vs. blast. Values represent mean ± SEM
