FIGURE 3.
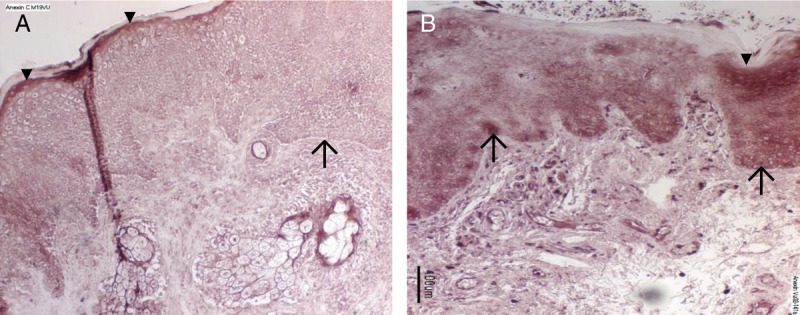
Immunostaining for annexin A1. Tissue samples from a representative control (panel A) and vulvodynia subject (panel B) were immunoreacted with anti-annexin A1 and detected with Vector Red. There is absent immunostaining in slides that were reacted with only the secondary antibody as controls (data not shown). Annexin A1 immunoreactivity (dark staining) is present in control subjects in a uniform distribution in the superficial layer of the epithelium (arrowheads; ▼) of the vestibular mucosa (panel A). In vulvodynia subjects compared with controls, annexin immunoreactivity in the superficial layer is more intense, but the staining pattern is more variable (panel 3B). In tissue from vulvodynia patients (panel 3B), the stratum basalis (arrows; ↑) displays an equally intense level of immunostaining to that of the superficial layer. However, staining is barely detectable in the stratum basalis of the control samples (panel 3A). In the vulvodynia samples, below the epithelium, there were also intensely stained lymphocytes present within blood vessels and scattered throughout the lamina propria.
