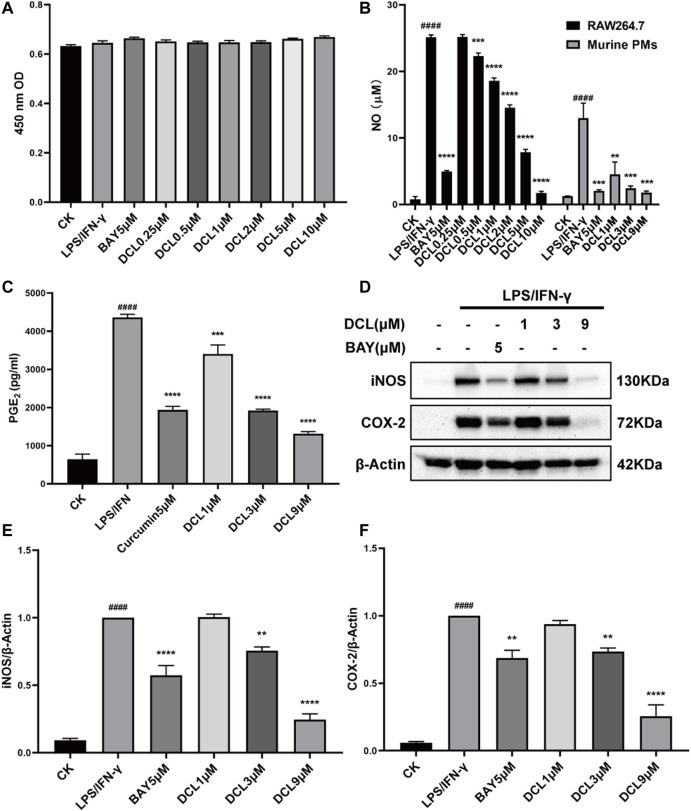
FIGURE 4.
DCL suppresses LPS/IFNγ-induced inflammatory response in murine macrophages. (A) Cell viability of LPS/IFNγ-stimulated RAW264.7 cells treated with different concentrations of DCL or BAY was measured by CCK-8 assay. (B) The effects of DCL on NO production in LPS (0.5 μg/ml)/IFNγ (10 ng/ml)-stimulated murine RAW264.7 macrophage cell line and murine primary PMs. (C) The effect of DCL on LPS/IFNγ-induced PGE2 release in RAW264.7 cells. (D) Western blot analysis of iNOS and COX-2 from RAW264.7 cells subjected to LPS/IFNγ stimulation and treated with different concentrations of DCL or BAY. The densitometry analysis of iNOS (E) and COX-2 (F), normalized against β-Actin. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, #### p < 0.0001 compared to the control check (CK) group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 compared to LPS/IFNγ group.