FIGURE 9.
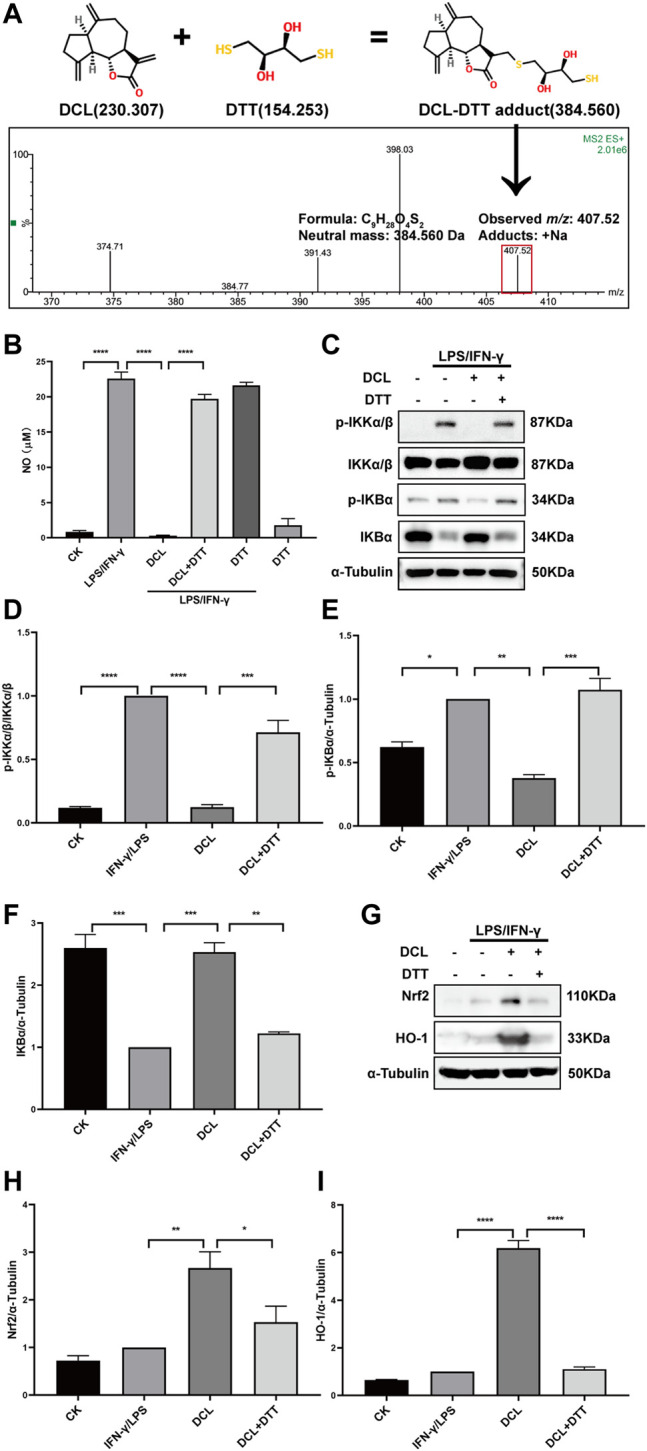
The α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone of DCL is important for its anti-inflammatory effects in LPS/IFNγ-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. (A) A possible Michael addition reaction between DCL and DTT is illustrated. The addition product of DCL and DTT was detected by LC-MS assay. (B) RAW264.7 cells were stimulated by LPS/IFNγ in the presence of DCL (9 μM) or DCL+DTT (50 μM) for 24 h and then the NO production was analyzed by Griess reagent. RAW264.7 cells were treated with DCL or DCL+DTT for 2 h, and followed by LPS/IFNγ stimulation for 5 min. The expression of p-IKKα/β, p-IκBα, and IκBα were detected by western blotting (C). The densitometry analysis of p-IKKα/β (D), p-IκBα (E) and IκBα (F), normalized against IKKα/β and α-Tubulin, respectively. RAW264.7 cells were treated with DCL or DCL+DTT for 1 h, and followed by LPS/IFNγ stimulation for 8 h. The expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 were measured by western blotting (G). The densitometry analysis of Nrf2 (H) and HO-1 (I), normalized against α-Tubulin. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.
