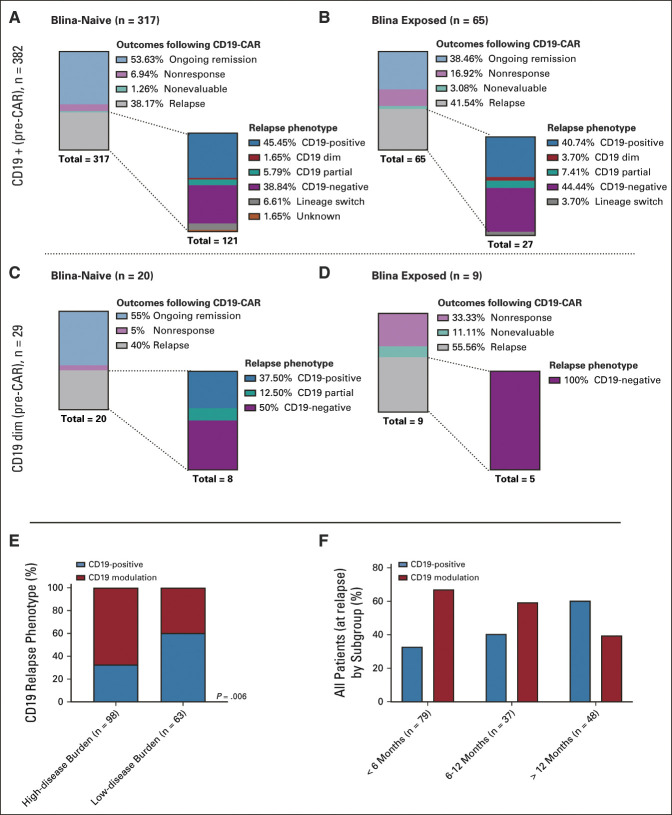
FIG 4.
CD19 modulation. Top: Patients with CD19-positive expression pre-CAR. (A) Outcomes following CD19-CAR for blinatumomab-naïve patients and subsequent CD19 immunophenotype at relapse. (B) Outcomes following CD19-CAR for blinatumomab-exposed patients and subsequent CD19 immunophenotype at relapse. Middle: Patients with CD19 dim expression pre-CD19-CAR. (C) Outcomes following CD19-CAR for blinatumomab-naïve patients and subsequent CD19 immunophenotype at relapse. (D) Outcomes following CD19-CAR for blinatumomab-exposed patients and subsequent CD19 immunophenotype at relapse. (Outcomes for patients with CD19 partial [n = 3] and CD19 status unknown [n = 6] are not shown. Among the CD19 partial population, one patient had received prior blinatumomab, and all three remain in an ongoing CR. Among patients with CD19 unknown expression, two had prior blinatumomab, three remain in an ongoing remission, three relapsed with CD19-positive disease [one had prior blinatumomab], one relapsed with CD19-negative disease [n = 1], and one relapsed with unknown CD19 expression. One patient was considered nonevaluable for response but emerged with CD19-negative relapse following initial disease assessment.) Bottom: CD19 expression at relapse. (E) CD19 expression at relapse, stratified by disease burden. (F) CD19 expression at relapse, stratified by time point of relapse post-CAR infusion. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; CR, complete remission.