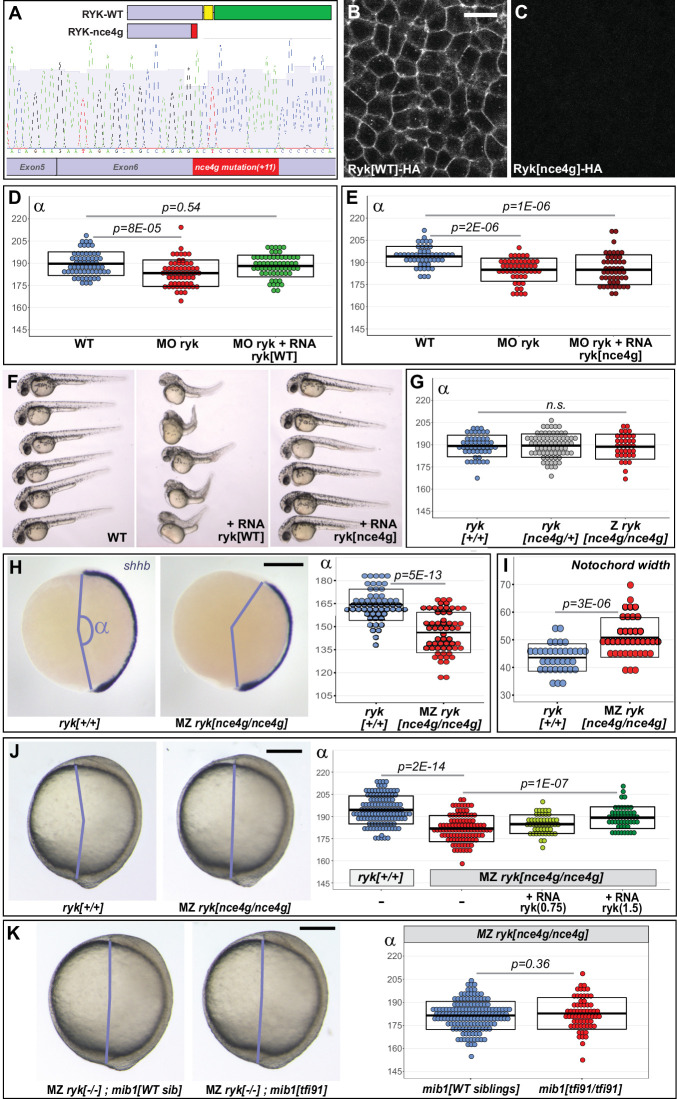
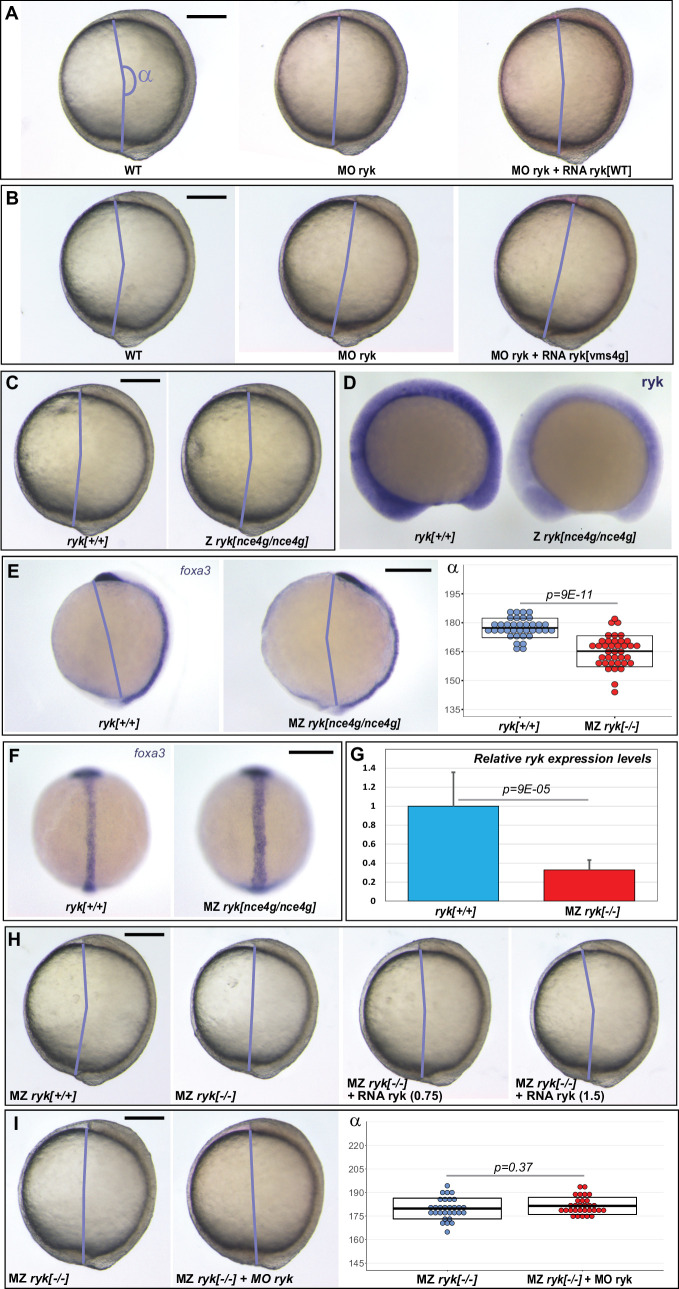
Figure 4. mib1 loss of function has no effect on convergent extension in maternal zygotic ryk mutants.
(A) ryknce4g mutants present an 11 base pair insertion in exon 6. The RYK-nce4g mutant protein comprises only part of the extracellular (blue) and lacks the entire transmembrane (yellow) and intracellular (green) domains. (B,C) Accordingly, a C-terminal HA tag that allows to localize WT Ryk (B, n = 12) becomes undetectable upon introduction of the ryknce4g mutation (C, n = 14). Dorsal views of 90% epiboly stage embryos, anterior up. Scalebar 20 µm. (D,E) The Convergent Extension (CE) phenotypes of ryk morphant animals can be rescued using 1.5 pg WT ryk (D) but not ryknce4g mutant (E) RNA. (F) Overexpressing high levels (25 pg) WT ryk RNA causes severe embryonic malformations while no effect is observed using ryknce4g mutant RNA. 32 hpf embryos, anterior to the left, dorsal up (n = 24 embryos/condition). (G) Zygotic (Z) ryk loss of function does not impair CE. (H–J) In contrast, Maternal Zygotic (MZ) ryk mutants present characteristic CE phenotypes such as a reduced axial elongation (H, shhb in situ hybridization) and an increased width of the notochord (I, foxa3 in situ hybridization, see also Figure 4—figure supplement 1F). (J) ryk WT RNA injection allows a significant rescue of MZ ryk mutant CE defects. (K) Similar CE defects are observed in MZ ryk single mutants and MZ ryk; mib1 double mutants. (H,J,K) Lateral views of bud stage embryos, anterior up, dorsal to the right. Scalebars 200 µm. In (D,E,G–K) boxes represent mean values ± SD. See Figure 4—source data 1 for complete statistical information.