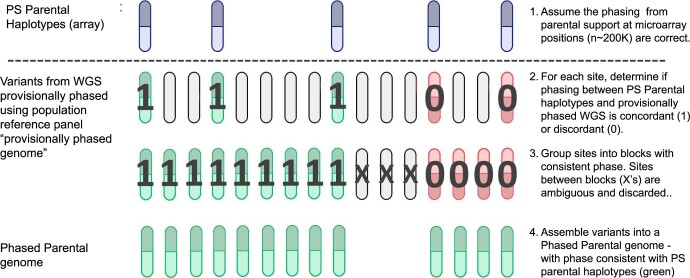
Extended Data Fig. 7. Obtaining a phased parental genome.
Each parent’s genome is phased using PS parental haplotypes (see Supplemental Note 1) and population reference panels using SHAPEIT4. The PS parental haplotypes serve as a scaffold (step 1) consisting of approximately 200,000 variants. WGS of both parents are provisionally phased using population reference panels and compared with PS Parental Haplotypes. Overlapping positions between the parental support haplotypes and provisionally phased WGS are marked as having concordant (1) or discordant (0) phase (step 2) and grouped into blocks (step 3). Interval regions between these blocks are suggestive of either meiotic recombination or error in phasing one or both parents; these sites are discarded (positions marked with ‘X’ in step 3). All remaining sites are used in subsequent assembly of the ‘Phased Parental Genome’ (step 4).