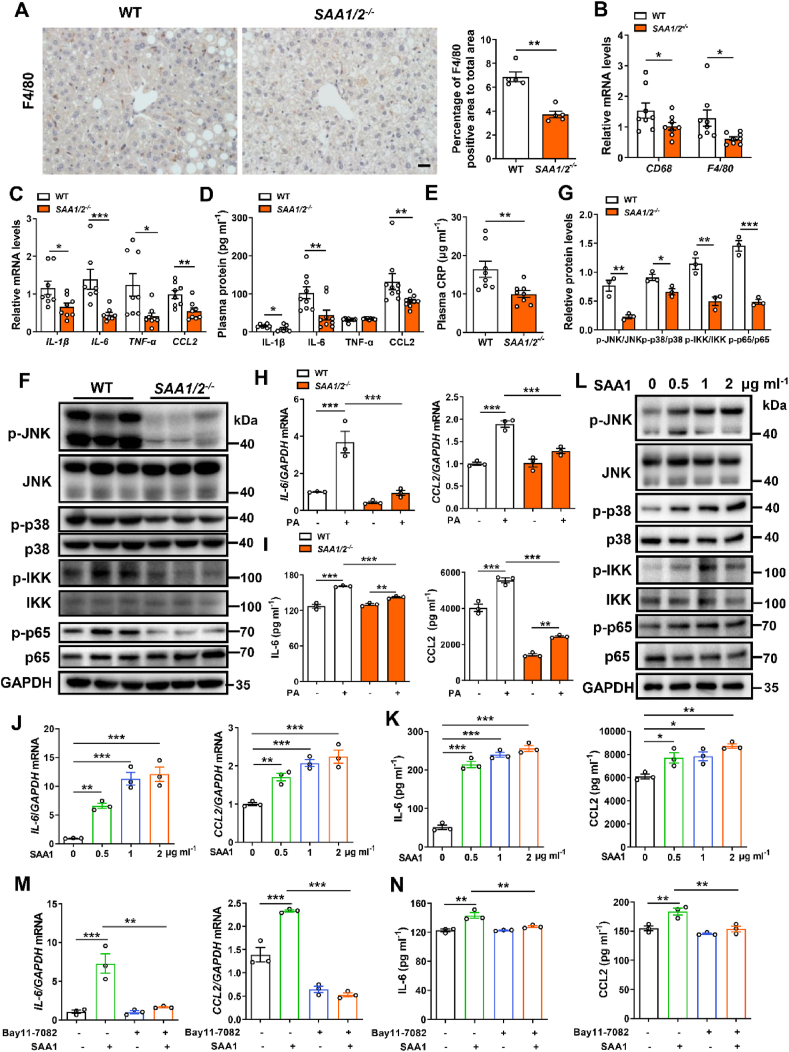
Figure 4.
SAA1/2 promotes hepatic inflammatory response. Male WT and SAA1/2−/− mice were fed a HFD for 16 weeks. (A) Representative IHC images (left) and quantifications (right) of F4/80 positive macrophages in the livers of WT and SAA1/2−/− mice (n = 5). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) mRNA levels of the markers of macrophages indicated in the livers of WT and SAA1/2−/− mice (n = 8). (C) mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and chemokine CCL2 in the liver of WT and SAA1/2−/− mice (n = 7–8). (D) Plasma concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and CCL2 in HFD-fed WT and SAA1/2−/− mice. IL-1β, n = 7. IL-6, TNF-α and CCL2, n = 9. (E) Plasma concentrations of CRP in HFD-fed WT and SAA1/2−/− mice (n = 8). (F, G) Representative western blot images (F) and quantifications (G) of the expression levels of key proteins in MAPKs and NF-κB signaling in the liver of HFD-fed WT and SAA1/2−/− mice (n = 3). (H, I) Hepatocytes isolated from CD-fed WT and SAA1/2−/− mice were treated with PA (0.25 mM) for 4 h mRNA levels of inflammatory mediators (IL-6 and CCL2) were assessed by qRT-PCR (n = 3) (H). IL-6 and CCL2 levels in hepatocytes culture media were determined using ELISA (n = 3) (I). (J, K) Hepatocytes isolated from CD-fed WT mice were treated with indicated concentrations of recombinant mouse SAA1 for 4 h mRNA levels (J) and culture media (K) of IL-6 and CCL2 were determined (n = 3). (L) Representative western blot images of the expression levels of key proteins in MAPKs and NF-κB signaling in hepatocytes that were treated with indicated concentrations of SAA1 for 30 min. (M, N) Hepatocytes isolated from CD-fed WT mice were treated with or without PA (0.25 mM) or NF-κB pathway inhibitor Bay-117,082 (10 μM) for 4 h mRNA levels (M) and culture media (N) of IL-6 and CCL2 were determined (n = 3). All data are expressed as means ± SEMs. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.