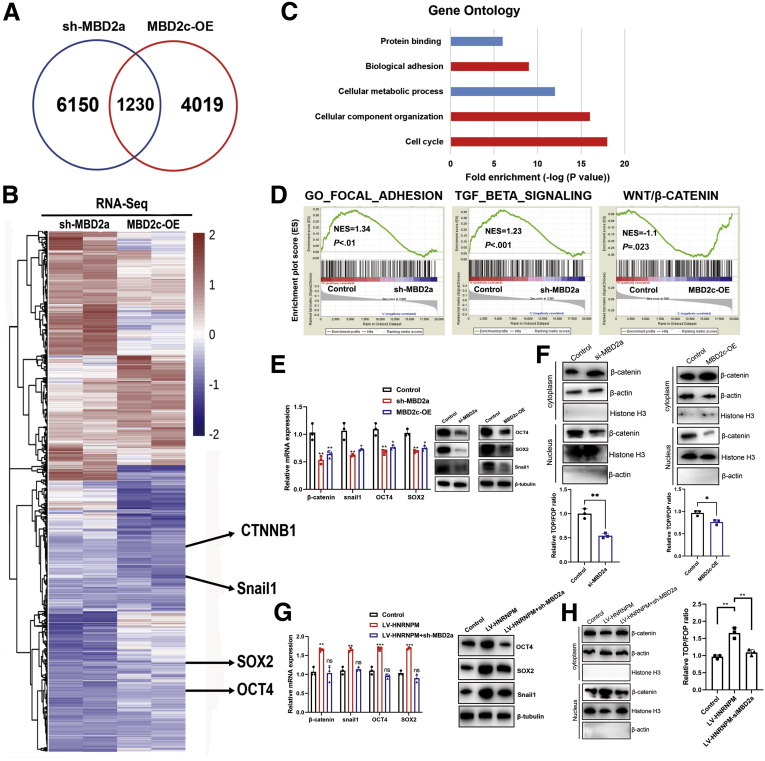
Figure 11.
The coregulated genes by MBD2a and MBD2c in HCC cells.A-B, Venn diagram of the RNA-seq data showing the genes commonly regulated by MBD2a and MBD2c. C-D, Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis. The top 5 GO terms in the indicated categories with the lowest P values are shown. E, The expression of Snail1, OCT4, SOX2 mRNA, and proteins was measured by qPCR and Western blot in MHCC97H cells expressing shRNAs targeting MBD2a, and in MHCC97H cells stably expressing MBD2c. Data were from 3 independent experiments. ∗P < .05 as compared with controls. F, The expression of β-catenin by nuclear/cytoplasmic protein fractionation and TOP/FOP-flash reporter assays when silencing MBD2a or overexpressing MBD2c. Data were from 3 independent experiments. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01 by the Student t test. G, The expression of Snail1, OCT4, SOX2 mRNA, and proteins was measured by qPCR and Western blot in MHCC97H cells expressing HNRNPM and shRNA targeting MBD2a. Data were from 3 independent experiments. ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with controls; ns, Not significant; P > .05. H, The expression of β-catenin by nuclear/cytoplasmic protein fractionation and TOP/FOP-flash reporter assays when overexpressing HNRNPM and silencing MBD2a. Data were from 3 independent experiments. ∗∗P < .01. P values were calculated using 1-way analysis of variance and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.