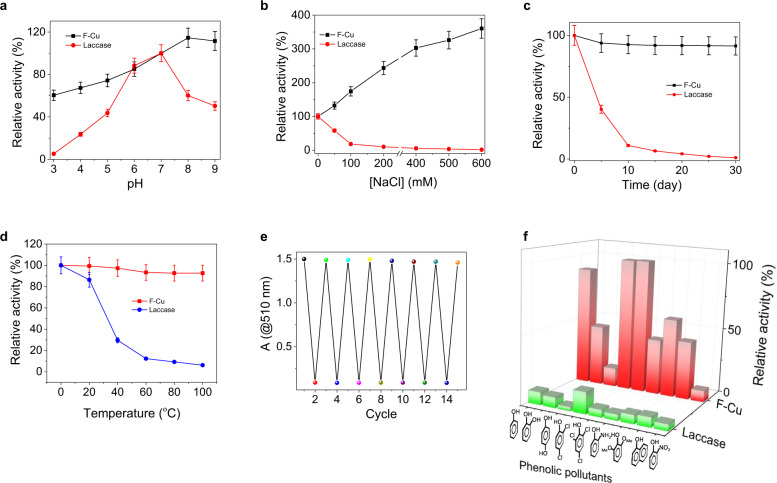
Fig. 4. Catalytic stability, reusability, and substrate universality of F-Cu bionanozyme.
a–d Relative activity of F-Cu and laccase under various a pH values (n = 3 independent experiments), b ionic strength (NaCl concentration, n = 3 independent experiments.), c storage time (n = 3 independent experiments), and d incubation temperature (n = 3 independent experiments). e Relative activity during the F-Cu recycling process (conditions for the recycling experiments: 0.6 mM 2,4- DP, 0.5 mM 4-AP, 5.04 × 10−6 mM (0.1 mg/mL) (F-Cu, pH 7.25, 25 °C, 1 h)). f comparison of relative catalytic conversion activity of the F-Cu bionanozyme and laccase based on the same weight (0.1 mg/mL) for various toxic phenolic pollutants (left to right: phenol, Catechol, Hydroquinone, 2,4- DP, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, 2-Aminophenol, 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol, 2-Naphthol, and 2-Nitrophenol). Error bars in all graphs represent standard deviations of three independent measurements.