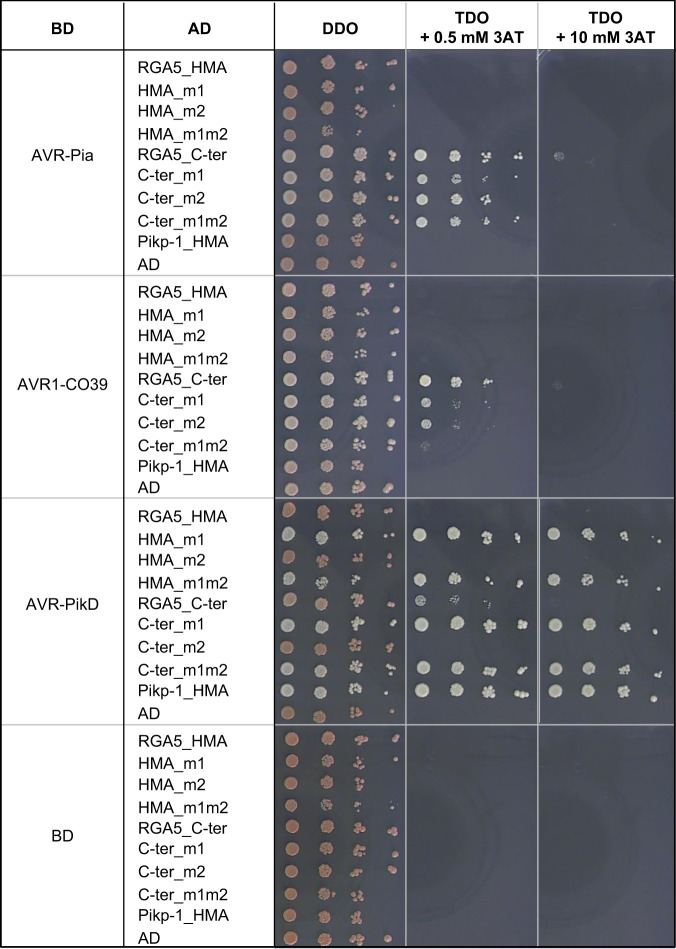
Fig. 2. Engineering of the HMA domain of RGA5 enables binding of AVR-PikD in yeast.
Interaction of AVR-PikD, AVR1-CO39, and AVR-PikD (without signal peptides and fused to the DNA binding domain (BD) of the GAL4 transcription factor) with the HMA (residues 991–1072) and C-terminal (residues 883–1116) domains of RGA5 and variants carrying mutations designed to introduce the AVR-PikD-binding surface (fused to GAL4 activation domain (AD)) was assayed by yeast two-hybrid experiments. The HMA domain of Pikp-1 (AD:HMA_Pikp-1) and the AD and BD domains alone were used as controls. Four dilutions of diploid yeast clones (1/1, 1/10, 1/100, 1/1000) were spotted on synthetic TDO medium (-Trp/-Leu/-His) supplemented with 0.5 mM and 10 mM of 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (3AT) to assay for interactions and on synthetic DDO (-Trp/-Leu) to monitor proper growth. Pictures were taken after 5 days of growth.