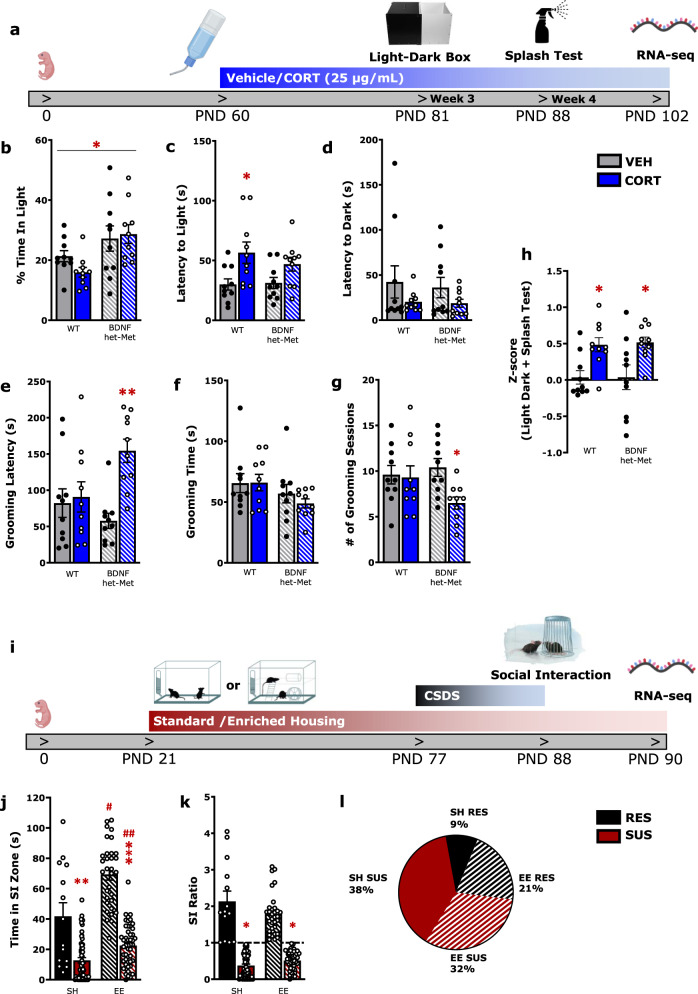
Fig. 1. Measurements of emotional behavior in the CORT model and CSDS model show similar face validity in male mice.
a Timeline for CORT treatment experiment. b–d Light–dark box test reveals increased anxiety-like behavior in mice treated with CORT. (2-way ANOVA, % Time in Light: genotype: F (1, 36) = 10.36, p < 0.01; Latency to Light: treatment: F (1, 36) = 11.47, p < 0.01). e–g Splash test reveals increased anxiety-like behavior in BDNF het-Met mice treated with CORT (2-way ANOVA, grooming latency: treatment × genotype: F (1, 36) = 6.523, p < 0.05; # of grooming sessions: treatment: F(1, 36) = 4.39, p < 0.05). h Complementary variables of behavior for both WT and BDNF het-Met were compiled to calculate a z-score, which show that CORT-treated mice displayed higher emotionality scores compared to vehicle-treated mice regardless of genotype (2-way ANOVA, treatment: F (1, 36) = 16.44, p < 0.001). i Timeline for CSDS treatment experiment. j, k The social interaction test reveals decreased anxiety-like behavior in RES mice. (2-way ANOVA, Time in SI Zone: interaction (susceptibility-by-housing) effect: F (1, 150) = 7.068, p < 0.01; SI Ratio: susceptibility effect: F (1, 150) = 243.2, p < 0.001). l Pie-chart depicting the proportion of mice raised in SH or EE and ranked RES or SUS after CSDS. The proportion of RES mice raised in EE (21%) was higher than the one of RES mice raised in SH (9%) (p < 0.05). Columns represent the mean ± S.E.M. of ten animals per group for the CORT model (a–h) and mean ± S.E.M. of 59 animals for SUS and 14 for RES in SH, as well as 49 animals for SUS and 32 for RES in EE (j, k). */#p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***/##p < 0.001. PND post-natal day, WT wild-type, BDNF het-Met heterozygous BDNF Val66Met, VEH vehicle, CORT corticosterone, CSDS chronic social defeat stress, SI social interaction, RES resilient, SUS susceptible, SH standard housing, and EE enriched environment.