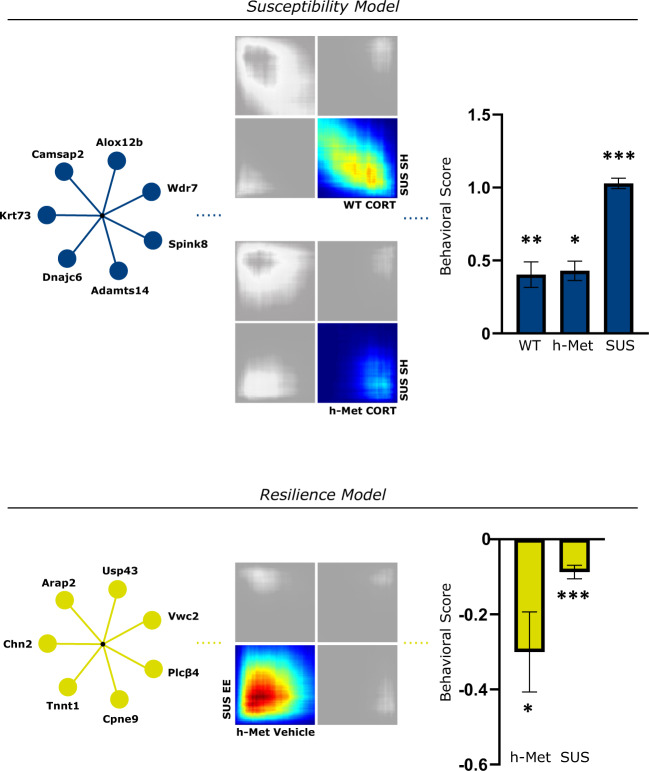
Fig. 5. Summary of transcriptomic and behavioral synchrony.
Enrichment in hub genes and DEGs in the cyan module, matching RRHOs, and behavioral susceptibility to stress (cyan column) are found in CORT-treated mice of both genotypes and SUS mice raised in SH. Enrichment in hub genes and DEGs in the yellow module, concordance in RRHO gene expression, and behavioral resilience to stress (yellow column) are found in BDNF het-Met treated with vehicle and SUS mice raised in EE. The behavioral score for each group was normalized to its respective control: WT CORT mice normalized to WT vehicle (t = 3.356, df = 17.95, p < 0.01), BDNF het-Met CORT mice normalized to BDNF het-Met vehicle (t = 2.579, df = 12.30, p < 0.05), SH SUS mice normalized to RES in SH (t = 5.454, df = 13.98, p < 0.001), BDNF het-Met vehicle mice normalized to BDNF het-Met CORT (t = 2.579, df = 12.30, p < 0.05), and EE SUS mice normalized to SUS in SH (t = 3.455, df = 104.6, p < 0.001). Behavioral score for each animal is calculated as: 1 − , where z = [(x − x̅cont)/σcont] * (±1)] and x = percentage time in the light, latency to dark, latency to light, grooming time, number of grooming sessions, grooming latency, time in social interaction zone, or SI ratio, and a = z for each respective control mouse. After calculation, a and z values where normalized to the lowest z score. Columns represent the mean ± S.E.M. of ten animals per group for the CORT model and mean ± S.E.M. of 59 animals for SUS in SH and 49 animals for SUS in EE. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. DEG differentially expressed gene, RRHO rank-rank hypergeometric overlap, WT wild-type, BDNF het-Met/h-Met heterozygous BDNF Val66Met, CORT corticosterone, SUS susceptible, SH standard housing, and EE enriched environment.