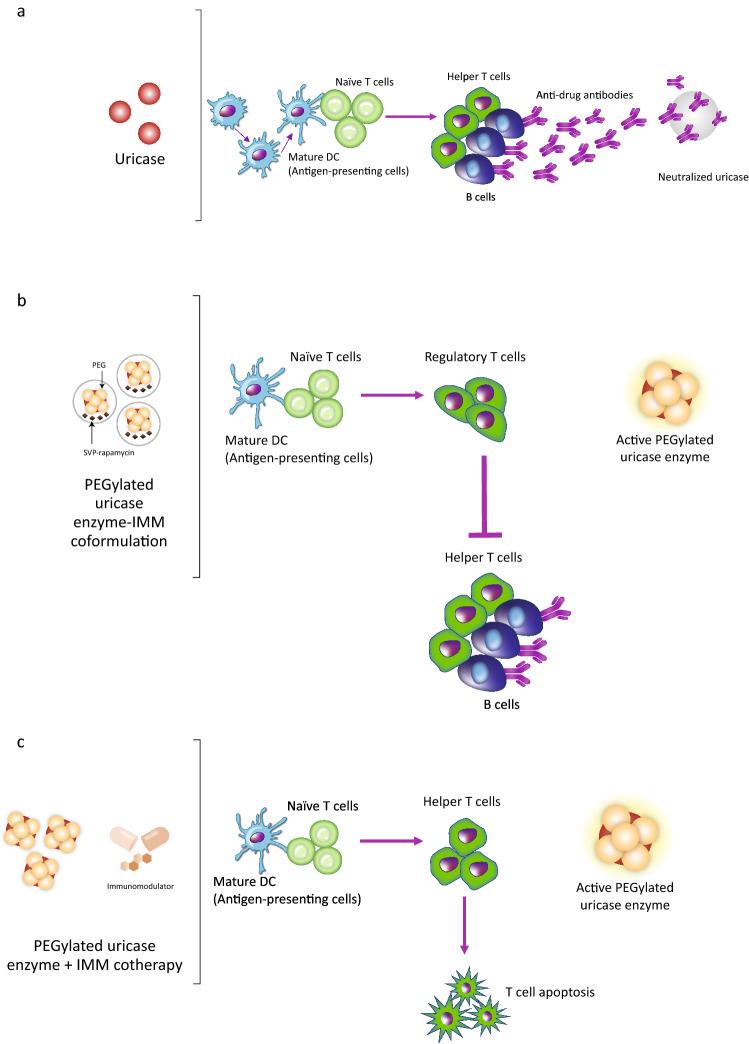
Fig. 1.
Immunologic response to uricase-based biologics in the presence and absence of immunomodulation [40, 28, 66–68]. (a) Uricase antigen uptake facilitates dendritic cell (DC) differentiation and maturation. In response to antigen presentation by DCs, T cells facilitate B-cell antidrug antibody production, followed by neutralization and proteolysis of uricase. (b) Exposure to a co-formulated system (e.g., PEGylated uricase enzyme encapsulated with SVP-rapamycin) induces DC tolerization to PEGylated uricase antigen. Tolerogenic DCs facilitate the production of anergic (or regulatory) T cells, dampening immunogenicity and prolonging PEGylated uricase activity. (c) Exposure to a PEGylated uricase enzyme with immunomodulation (IMM) co-therapy (e.g., oral methotrexate) increases T-cell sensitivity to apoptosis, disrupting the pathway to immunogenicity. Figure adapted from Brunn et al. 2021 [55]. Molecular images of uricase and PEGylated uricase enzymes are not representative of molecule shape or structure and are for illustration purposes only