Figure 3.
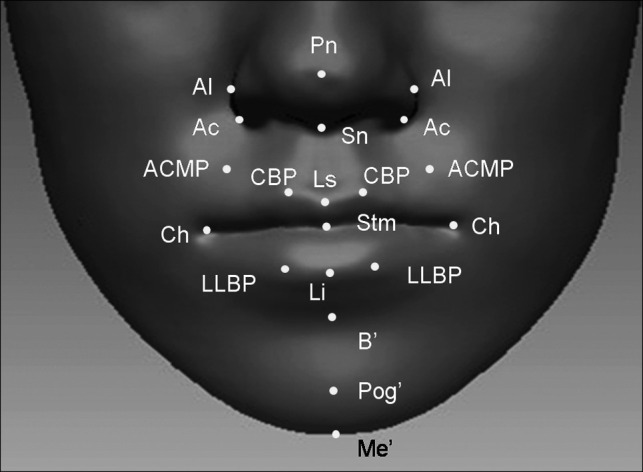
Soft tissue landmarks. Nose-related: pronasale (Pn, the most protruded point of the soft tissue nose); subnasale (Sn, the midpoint of the angle at the columella base where the lower border of the nasal septum and the surface of the upper lip meet); nasal ala (Al, the most lateral point on each alar contour); alar curvature point (Ac, the most lateral point in the curved base line of each ala, indicating the facial insertion of the nasal wingbase). Upper lip-related: labrale superius (Ls, the midpoint of the upper vermilion line); cupid bow point (CBP, the most elevated point of the philtrum on the upper vermilion border line); alar curvature-cheillion midpoint (ACMP, the midpoint between ala curvature and cheilion). Lower lip-related: Labrale inferius (Li, the midpoint of the lower vermilion line); lower lip bow point (LLBP, the breakpoint on the lower vermilion border line). Stomion-related: stomion (Stm, the point at the midline of labial fissure between gently closed lips); cheilion (Ch, the point located at each labial commissure). Chin-related: soft tissue B point (B′, the deepest point on the facial midline, between the lower lip and chin); soft tissue pogonion (Pog′, the most anterior midpoint of the chin); soft tissue menton (Me′, the lowest median landmark on the lower border of the mandible).
