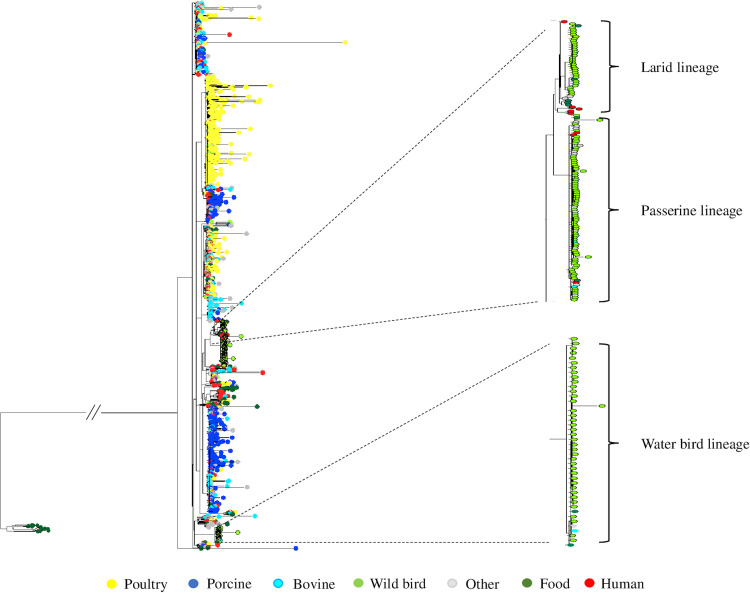
FIG 3.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of 1,604 S. Typhimurium isolates from different sources for zoonotic source prediction. The maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree for zoonotic source prediction includes S. Typhimurium isolates from seven source classes: (i) bovine (n = 195), including isolates from cattle, beef, and raw milk; (ii) porcine (n = 338), including isolates from pigs and pork; (iii) poultry (n = 440), including isolates from chickens, turkeys, ducks, and their eggs; (iv) wild bird (n = 199), including 131 isolates from this study; (v) human (n = 171), including human clinical isolates; (vi) food (n = 83), including seafood, plant-based food, and other ready-to-eat and/or processed food; and (vii) other (n = 178), including any isolates not belonging to the aforementioned classes. The larid, passerine, and water bird lineages formed by the S. Typhimurium isolates from wild birds are enlarged and highlighted in the phylogenetic tree.