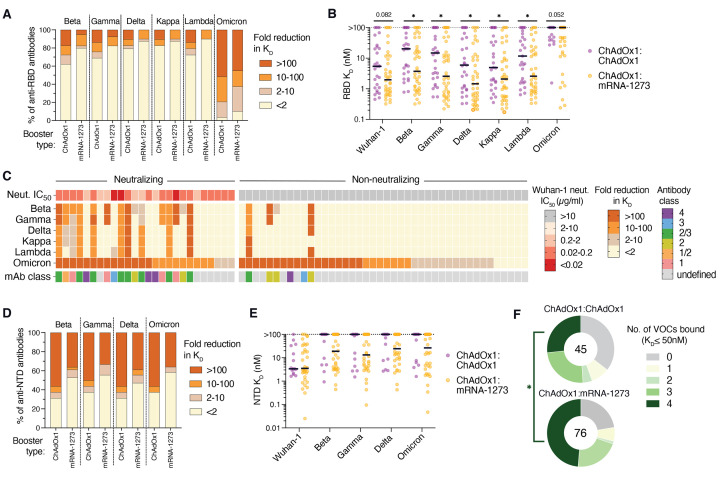
Fig. 4. Breadth of antibody binding to SARS-CoV-2 variants.
(A) Proportion of anti-RBD antibodies with the indicated fold reduction in Fab binding affinity to RBDs incorporating mutations present in the Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, Lambda, and Omicron variants relative to the Wuhan-1 RBD, as determined by a bead-based flow cytometric assay. (B) Fab binding affinities of anti-RBD antibodies to Wuhan-1 and variant RBDs. Antibodies that did not reach half-maximal saturation at the highest concentration tested (100 nM) are shown as KD >100 nM. Black bars denote medians. (C) Heatmap showing the fold reduction in affinity to variant RBDs compared to the Wuhan-1 RBD among neutralizing and non-neutralizing anti-RBD antibodies. The top bar indicates the neutralization IC50 of each mAb against MLV-SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-1. Antibodies that did not reach 50% neutralization at 10 μg/ml were classified as non-neutralizing. The bottom bar denotes the class of each anti-RBD antibody. (D) Proportion of NTD-directed antibodies with the indicated fold reductions in binding activity to variant NTDs relative to the Wuhan-1 NTD. (E) Fab binding affinities of anti-NTD antibodies to Wuhan-1 and variant NTDs. Antibodies that did not reach half-maximal saturation at 100 nM are shown as KD >100 nM. Black bars denote medians. (F) Combined proportions of anti-RBD and anti-NTD antibodies that bound the indicated number of variants of concern (Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron) with KD ≤50 nM. The number in the center of the pie indicates the total number of antibodies tested. Statistical significance was determined by [(B) and (E)] two-sided Mann-Whitney U tests or (F) Fisher's exact test. N.B., non-binding; KD, equilibrium dissociation constant; IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration. *P < 0.05.