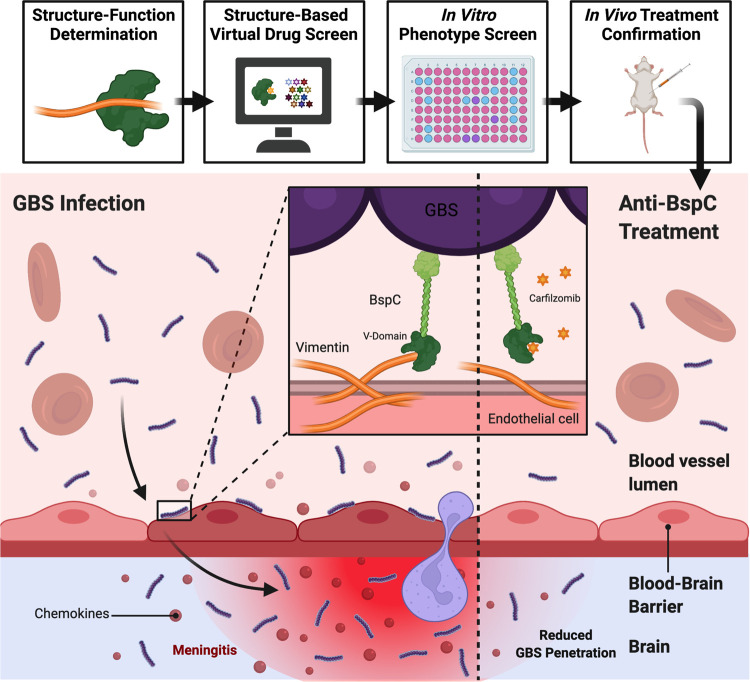
Fig 8. Summary of Anti-BspC Treatment to Reduce the Pathogenesis of GBS Meningitis.
GBS utilizes BspC to interact with vimentin expressed by endothelial cells to adhere to the BBB endothelium and cause meningitis. Site-directed mutagenesis identified a vimentin-binding pocket contained within the BspC V-domain. This structure-function determination informed a virtual drug screen that yielded a list of drugs, two of which were confirmed to block BspC dependent adherence brain endothelial cells in vitro. Of these drugs, Carfilzomib was the most effective and was also able to prevent GBS entry into the brain in vivo. Figure generated using BioRender.